I'm a gamer, and all gamers know that RGB lighting makes your PC go faster, so it's critical for every build. But each manufacturer has its own proprietary control software, and they don't play nicely together.
I want one program that gives me control over all the pretty lights, not three terrible apps that I have to tweak individually while they take turns at the all-you-can-eat RAM buffet. I can use middleware to connect the lights from different components and make sure they behave.
In business, middleware acts as a translation layer in your tech stack, helping apps communicate when they otherwise couldn't. It translates requests, formats data, and bridges closed systems.
In this article, I'll cover types of middleware and how middleware integration works. I'll also go over a few ways to help you keep your data consistent across infrastructures and keep your teams working smoothly together, just like my LEDs. Sure, I might be losing to 12-year-olds on Fortnite, but my computer looks great doing it.
Table of contents:
What is middleware integration?
Middleware makes disparate applications, systems, and services work together. It can connect enterprise platforms to break down data silos and keep teams aligned.
Integrating middleware means controlling the flow of data and communication between apps, enabling multi-stage automation. You can use it to automatically enrich partial data from multiple sources into a single source of truth that stays current no matter where an update happens.
You've probably set your sights a little higher than a smooth water effect with your lighting. Maybe you wish your CRM and ERP systems were more closely integrated so that you can help departments using different software to collaborate. Middleware can automatically sync data between them to enhance sales collaboration.
For example, you could:
Set up a connection that updates Salesforce contacts whenever there is an update in NetSuite records.
Keep your sales funnel updated in real time by automatically creating new deals in HubSpot when a new record is added to NetSuite.
Update record in NetSuite to automatically update contacts in Salesforce
Create new HubSpot deals from new NetSuite records
Zapier lets you build AI workflows that automate interactions between all your apps, removing bottlenecks and orchestrating systems across your business. The examples above are just the start. You can build more complex solutions—all with no-code—including AI agents.
How does integration middleware work?
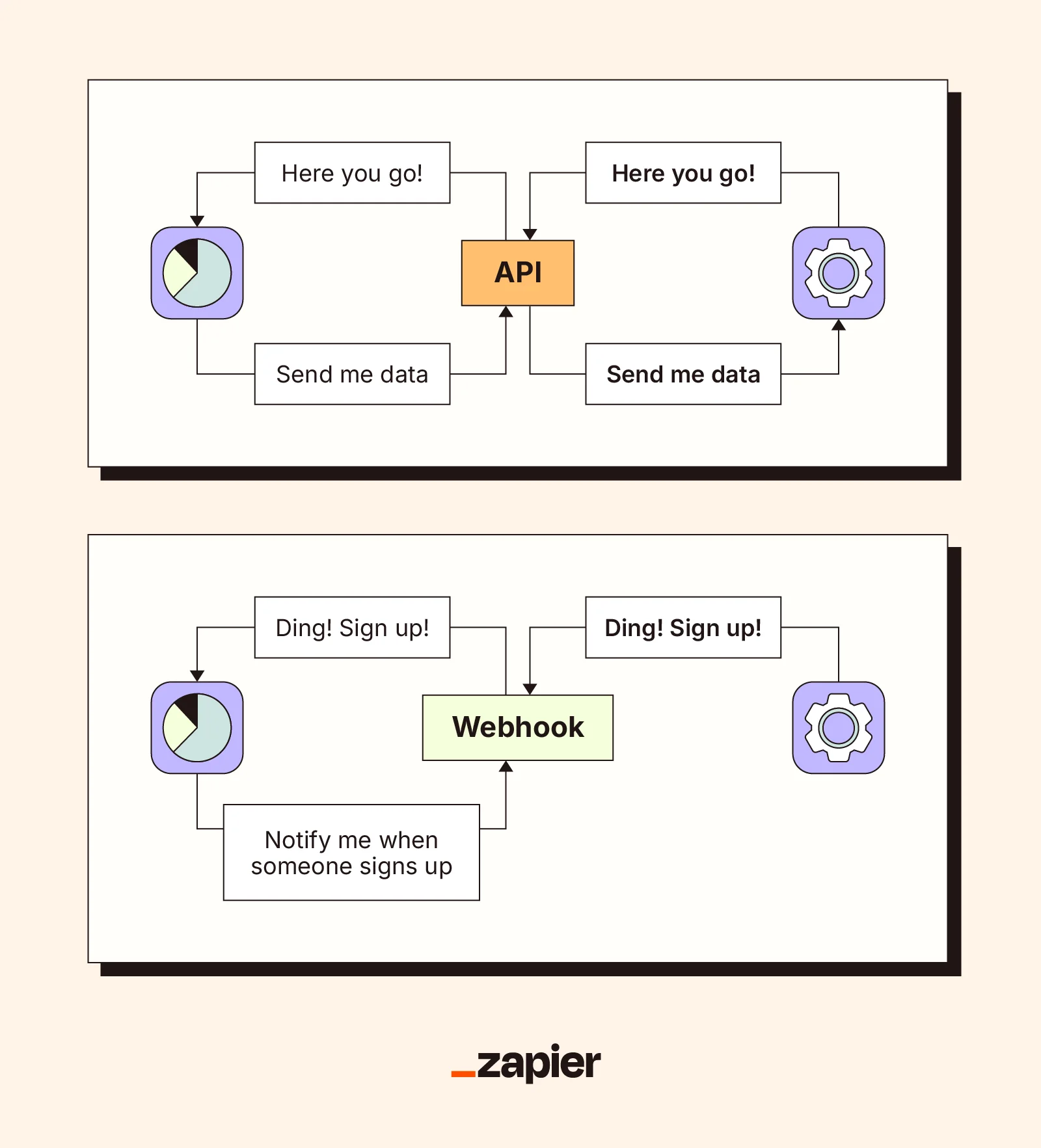
Middleware is the behind-the-scenes software layer that helps two (or more) systems communicate without needing to be directly wired to each other. Before we get into it, you need to understand these key terms: servers, clients, APIs, and webhooks.
A server runs the programs or hosts data that you need access to (a website or an app).
A client is a program or user interface that wants to access data from a server.
An API runs on the server or host app. It allows clients to make requests using a set of rules, then sends responses when it receives a valid request.
Webhooks are event-based versions of APIs that work in the opposite direction. They trigger when an event occurs on a server and automatically send updates to connected clients.
At a high level, middleware integration works by taking requests or events from one system, applying rules and transformations, and then passing them to another system in the form it expects.
A typical flow looks like this:
A request or event kicks things off: This could be a client making an API request ("create a new customer record") or a server sending a webhook ("a new order was placed"). On Zapier, this happens based on activity in an app or on a schedule.
Middleware receives the data and validates it: It checks that the request is allowed, that required fields are present, and that the sender is authenticated (for example, using API keys, OAuth tokens, or signed webhook payloads).
Transform and map fields: Different apps represent the same information in different ways—field names, data types, and structures rarely match—so middleware reformats data into what the next system expects. On Zapier, this happens with Zapier Formatter.
It routes data to the right place: Middleware sends the data to one or more destinations via APIs, sometimes conditionally (e.g., "only send enterprise leads to the CRM"). The conditional aspect on Zapier can happen with Filters or Paths.
It handles reliability concerns: When requests fail due to timeouts, rate limits, or downtime, middleware often retries, queues work until systems recover, and logs what happened so you can debug it. On Zapier, you can even set specific error handling rules.
It passes the request along and returns the outcome: Finally, middleware forwards the transformed request to the destination system and either returns a response to the client (API-style) or records the result of processing the event (webhook-style).
Different apps store data differently, and the ways to access that data change over time. Middleware makes integration less brittle by absorbing those differences, so systems can keep talking even as APIs evolve, payloads change, or traffic spikes.
Zapier uses APIs and webhooks under the hood. You can build multi-step AI workflows with logic, routing, and timing across tools, all using natural language:
Extract and format data automatically.
Add conditional logic to automated workflows to create nested paths.
Use tables to keep workflow data organized and create more reliable AI automations.
Filter events based on custom parameters, like deal size.
Delay and schedule communications between apps.
With Zapier Copilot, you can use natural language to tell Zapier what you want to achieve, and it'll help build the solution for you.
Key types of integration middleware
Middleware has different purposes and functions depending on the use case. Some types of middleware are just translation layers that forward events, while others add logic between the applications. You can also use middleware software platforms that act as a central control for your apps.
These are the major types of middleware.
Integration platform as a service (iPaaS)
An iPaaS is a cloud-based software platform offered as a service. It's intended to be a central suite of tools that you use to synthesize and control data across multiple applications, data sources, and IT environments.
Solutions like Zapier feature low- or no-code prebuilt connectors for thousands of apps, making them great for complex tech stacks as well as teams with few IT resources.
Used for: Any size business that wants a scalable, low-development automation solution.
Enterprise service bus (ESB)
ESBs are architectures that facilitate communication and data exchange between apps. They're communication layers between programs that translate data into a single canonical format, most often used for enterprise application integration.
ESBs generally focus on message-level integration, acting as a consistent layer between apps, while iPaaS solutions tend to focus on API connections and automations.
The bus system is similar to, but distinct from, API gateways that iPaaS solutions use. ESBs are often used on location within enterprises and require dedicated IT resources to set up and maintain.
Used for: Large enterprises with multiple IT infrastructures, on-site servers, or complex tech stacks.
Message-oriented middleware (MOM)
Message-oriented middleware is a type of middleware system that acts as a communication layer between apps. It's the design principle that ESBs are based on: all messages should be translated into a single canonical language and transmitted across a central network.
This decouples direct app connections, making it ideal for complex environments, such as multiple legacy IT environments that need to communicate with each other.
Used for: Enabling communication between disparate systems and establishing canonical data formats.
API gateways
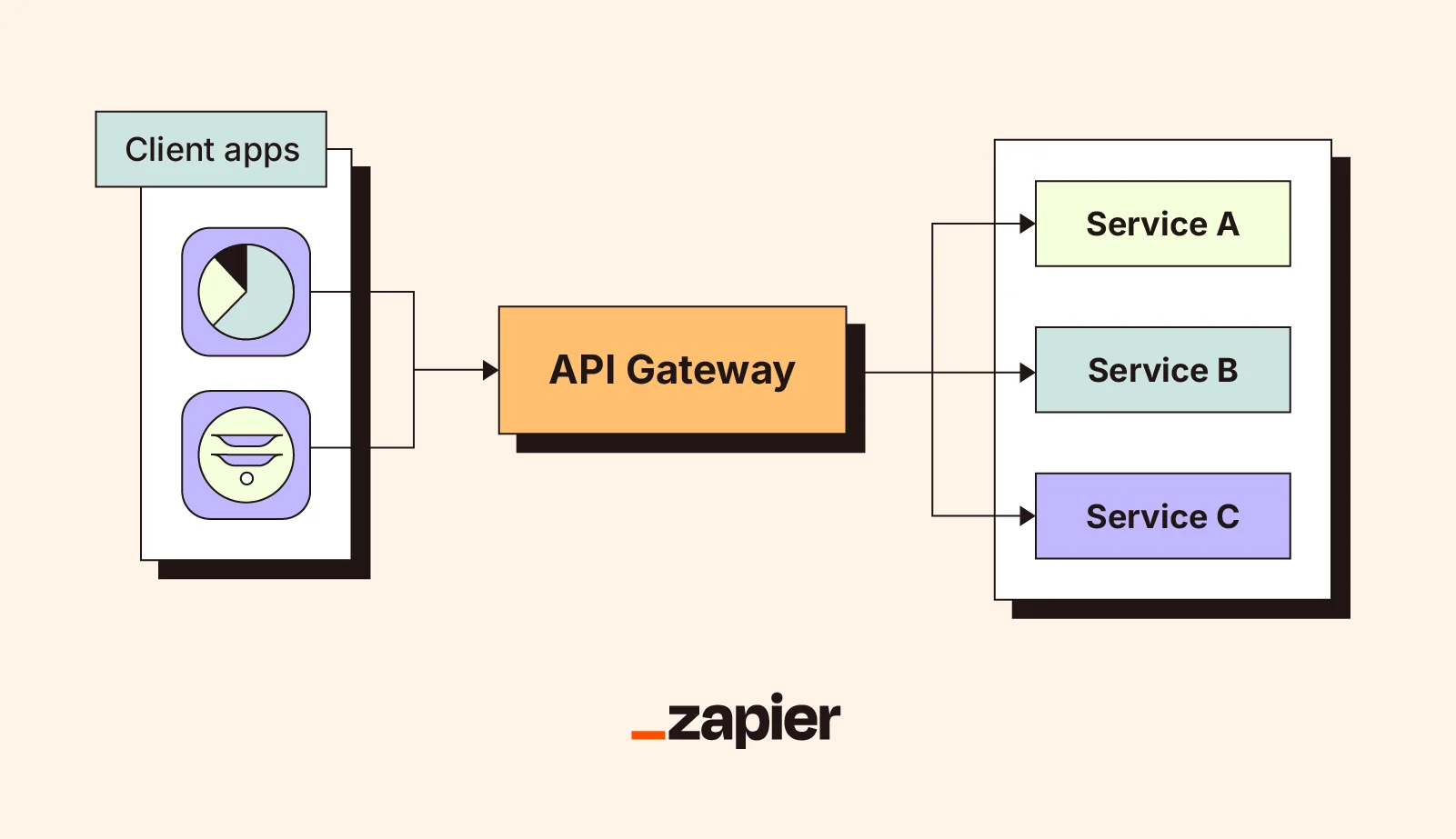
An API gateway is a central point that manages API requests from clients to services. It can manage interactions between multiple clients and applications, directing requests to the appropriate service. This eliminates the need for direct app-to-app API connections, acting as a third party that can apply logic, authenticate clients, and provide security.
API gateways reduce the number of connections a system needs, which helps reduce code complexity and vulnerability to attack.
They protect apps from having multiple sources of direct access and vulnerability. It's like using a doorbell camera to see who's knocking. Just because I've let someone in once doesn't mean I want them crawling through my window whenever they want to talk to me.
Used for: Controlling how and when clients can make requests through API connections.
Data middleware
Middleware data integration provides a centralized database service between systems. They can help different backend systems communicate and synthesize data, as well as provide database functionality to front-end systems.
Used for: Streamlining access to backend databases.
Event-driven middleware
Event-driven architecture involves middleware that creates and communicates events between different apps. Instead of having the apps communicate directly with each other, the middleware detects changes and applies logic to trigger automations.
This software lets you control the automations directly instead of relying on how the apps interpret one another, which can be limited or change with updates.
Used for: Building customized, multi-stage workflows that depend on certain events and parameters.
Robotic process automation (RPA) middleware
Robotic process automation uses software bots to perform rules-based tasks like data entry. These bots perform simple, repetitive tasks that would ordinarily require a person to numb their brain, staring at a spreadsheet for a few hours. As part of middleware solutions, they can send messages, update data tables, and do many other tasks, especially in graphical user interfaces.
Used for: Automatically performing data entry and organizational tasks as part of workflows.
Benefits of middleware integration
Middleware provides a foundation to integrate new tools with legacy systems. It allows you to take control of the communication and orchestration when applications don't report the events that you want or respond to the inputs you need them to.
Integrating middleware lets you:
Decide what events trigger specific workflows and connect apps into chains.
Create rules-based alerts and automations based on custom criteria (such as purchase size, ticket type, etc.)
Automatically update data between different databases to ensure that your teams have a single source of truth.
Keep all your software communicating, even when APIs get updated or services experience downtime.
Implement access controls for workflows and apps.
Reduce the need for multiple access points and licenses to save money on subscription fees.
Implement AI agents and chatbots into workflows and control what information they have access to.
For example, you can use Zaps to connect multiple lead sources to HubSpot and dig yourself out of data entry hell. Capture the lead and standardize the data, whether it comes from Facebook, TikTok, Google Ads, or anywhere else.
Or you could create an AI call coach that connects Gong and Slack to Zapier's tools: Tables, Code, and AI. Call transcripts are automatically analyzed, and feedback is provided directly in Slack. It also pings managers for low-scored calls. No more waiting for feedback, and managers can prioritize the most critical training opportunities.
Automate personalized coaching for your sales team using this AI-powered call analysis template.
Examples of middleware
Alright, enough hypotheticals. Let's look at some real middleware examples from real Zapier customers.
Sales and marketing
Leads come in from multiple sources. When there's a lot of volume from different sources, synthesizing the data into a form your sales team can use takes time. If it takes too much time, the leads might go cold.
For example, Veo, a sports-focused camera brand, takes in thousands of leads each month from social media and email. Manually pulling the data took a ton of labor and thousands of hours. So they built automations with Zapier to automatically import lead data into their CRM as it comes in.
The automatic migration allows them to follow up on tens of thousands of leads per month, with thousands of work hours saved.
Customer service
Customer service can involve a lot of unnecessary work. It's easy for agents to have their time wasted by repetitive or irrelevant tickets that they nonetheless must evaluate, leaving less time for users with critical issues.
Middleware can help ensure tickets get sent to the right teams, as well as provide automations that prioritize tickets based on urgency, sentiment, and other factors.
To help support agents focus on high-priority issues, Otter.ai used Zapier and ChatGPT to automatically resolve repetitive and unnecessary tickets. The automation also tags and triages tickets so that agents can work based on issue priority and customer sentiment. This lets them focus on critical issues first and saves multiple hours each week.
Human resources
One job. Thousands of applicants. A recruiter with a headache. If your recruiters spend more time organizing candidate profiles than they do reviewing them, you might need an automation.
At JBGoodwin REALTORS, recruiters spent up to 25% of their time manually entering data for applications. They created multi-step workflows using Zapier, HubSpot, Gmail, and AI by Zapier to automatically fill and enrich applicant information. This helped recruiters save hours each week and increased recruiting 37% year-over-year.
IT
Remember what I said about thousands of applicants? Meet the original headache-havers: helpdesk and IT. Triage gets impossible on an ever-growing mountain of requests, so important issues get buried.
Zapier can give your IT team relief by setting up ticket systems, automated notifications, and triage to prioritize the biggest issues. For example, Remote, a global HR platform, saves $500k each year with an AI-powered help desk. It automates tickets across multiple messaging systems, and the AI even helps suggest resolutions.
Here's a template that mimics Remote's setup.
Improve your IT support with AI-powered responses, automatic ticket prioritization, and knowledge base updates.
Use Zapier for middleware integration
For me, harmonious lighting between my Corsair and NZXT hardware lets me build my cool fire effects in one place, not two. For businesses, middleware helps teams keep updated and avoid stepping on each other's toes.
Zapier is a middleware service that can also help you connect systems and build new workflows across departments and infrastructures. You can combine fragmented data into a single source of truth, automate daily feedback so that reps don't have to wait, or task an AI workflow to discover sales opportunities in support tickets.
With connections to over 8,000 apps, Zapier can help businesses of any size orchestrate complex workflows from start to finish.
Related reading: