A customer journey map is a visual representation of the complete experience a customer has with a product, service, or brand—from the first moment they become aware of it, all the way through purchase and long-term use.
When I was a kid, I remember watching my parents switch between different credit cards to get the best rewards for a particular purchase. They almost always pulled out the American Express first because, as they explained to me, the base reward rate was higher than even the sector-specific perks offered by other cards. Twenty years later, when I decided to get a high-end credit card, Amex was the first one that came to mind.
Experiences like this don't happen by accident. They're shaped by countless moments that influence how someone hears about, evaluates, and eventually chooses a brand. Customer journey mapping is the process of understanding and planning those moments—from the very first impression all the way through a long-term relationship.
Here, I'll dive into everything you need to know about customer journey mapping. Plus, a few examples and templates to help you create your own map.
Table of contents:
What is a customer journey map?
A customer journey map is a visual representation of the grand journey your customer takes from awareness to prospective buyer to loyal and devoted customer.
The journey is split into two parts: the buyer journey and the user journey. The buyer journey covers everything up to the point of purchase. After that point, the customer becomes a user, and all of their experiences are part of the user journey.
The overall journey may take many twists and turns through the hedges of social media to the fires of Mount Sales. But with a customer journey map, you'll never have to wonder where you (or your customer) will end up.
How to create a customer journey map
Creating a customer journey map is all about breaking the experience down into simple, understandable steps so you can see where customers succeed, where they get stuck, and where you can make meaningful improvements. Let's walk through each step of the process, from setting your goals to sharing your finished map.
If you already have a template or structure you like to use, awesome. If not, pick one of our templates below before diving in.
1. Define objectives
The first step is to identify the goals of the customer journey map. Start by asking yourself these questions (or similar ones):
Do you want to sell more products to a specific customer base?
Do you want to close more of your existing deals?
Do you want to find out why no one is adopting the latest addition to your product or service?
Understanding your goals is crucial to making the most of this mapping exercise because they help establish trajectories, timelines, and key performance indicators (KPIs). You need to know what wins will have the sales team at your desk with confetti, and which ones won't move the needle quite as much.
2. Create personas
If you don't already have customer personas created, now is the time to do it. Develop two to three detailed customer or user personas representing your target audience, and use these personas in your customer journey mapping exercise.
Some good questions for this stage in the process include:
Why are people using your system, product, or service?
What problems do people use your product to solve?
How, when, and where do they use your product or service?
These hypothetical users should help you visualize how individuals discover and interact with your brand and why they might look to your products over competitors' or to solve specific pains with no current solutions.
3. Collect data
Grab your metaphorical shovel and dig into the data. Reach out to sales, marketing, or customer experience teams to find out more about the journey itself. You can gather qualitative and quantitative data from customer feedback, past marketing campaigns and sales figures, and third- or first-party market research that will make your customer map more accurate.
Here are some examples of data you'll want to collect:
Stages of the sales process
Common sales pain points
Market segmentation criteria
Customer feedback on the sales and support processes
Any other information your teams suggest including in your map
4. Map stages
Once you know your objectives and the hypothetical customers you want to achieve them with, you'll get out your customer map (and all that delicious data you just collected) and list all touchpoints where customers interact with your brand. These should fit, at least loosely, into one of five customer journey stages:
Awareness: This is when prospective buyers first learn your brand or product exists.
Consideration: This is when your prospective buyers compare options and decide whether your solution fits their needs.
Conversion: This is when prospective buyers take the key action you're aiming for, such as making a purchase or signing up, and officially become customers.
Retention: This is when customers continue using your product and experience ongoing value.
Brand loyalty: This is when they become repeat customers or advocates who recommend your product to others.
Depending on the complexity of your sales and marketing strategies, your brand may have additional stages to include in that list or may have substitutions. But for most products or services, these five are pretty fundamental to successful, repeatable sales processes.
5. Visualize and analyze
Using your customer journey data and newfound insight into the stages of your brand's sales process, you can now build out a visual map of the customer journey. Do this using one of our templates or by using your own research as inspiration to plot a map tailored to your products or services.
6. Share and revise your map
Once you've filled out your map, it's a good idea to share it with relevant team members to get feedback on touchpoints from their perspectives. For example, your marketing team might notice that some personas are more likely to interact with your brand via social media than PPC ads. Or your UX team might suggest that some target personas are likely to be interested in a product feature you hadn't thought to connect them to.
Customer journey map templates
Here are some map templates for common customer journeys. You can customize each of these to fit the individual needs of your personas. Singing "The Road Goes Ever On" as you set out is optional but encouraged.
General customer journey map template
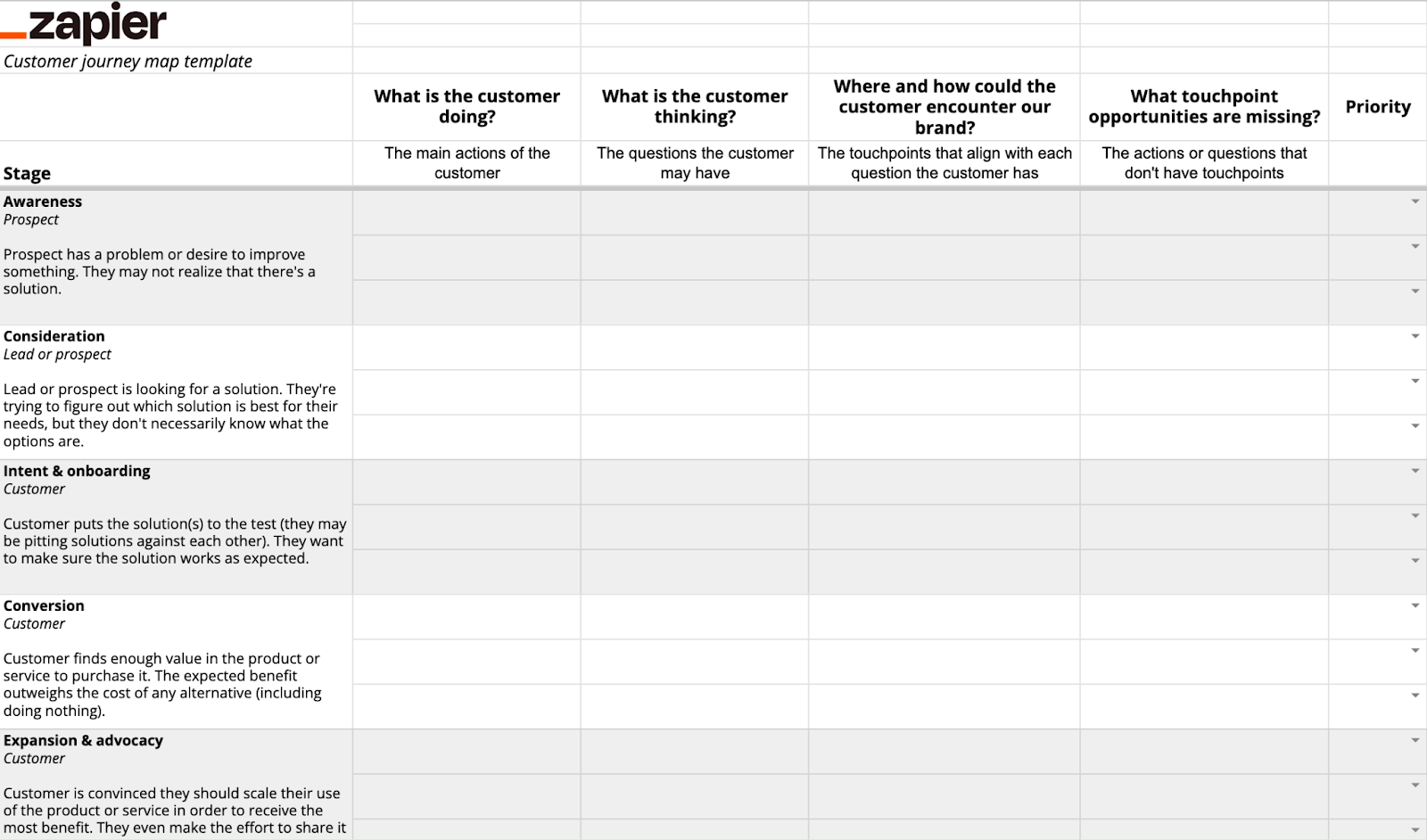
This customer journey map template is separated into five stages along the leftmost column, with guiding questions to help plan the customer's experience in each stage. Make a copy of the Google Sheets file, and then you can easily tweak it to match your preferred stage names and questions.
Day in the life map template

A great way to map mini-journeys within the larger customer experience lifecycle is with a "day in a life" journey map. This map plots the same things as the general customer journey map—key milestones, questions, touchpoints, and gaps—but over a particular period of time instead of over the course of the entire relationship.
Customer support journey map template

Another side of the customer journey coin is the support journey. This journey map is a bit different in that it doesn't just map touchpoints; it maps functional interactions between the customer and customer service representatives as well as the behind-the-scenes activities necessary to support the customer-facing team. It also gives you space for summary notes to help you focus on high-level staging structure.
Customer journey map examples
A blank page is inspiring (said no one ever), but to help you get a better sense of what the end result might look like, here are some examples of completed customer journey maps.
General customer journey mapping example

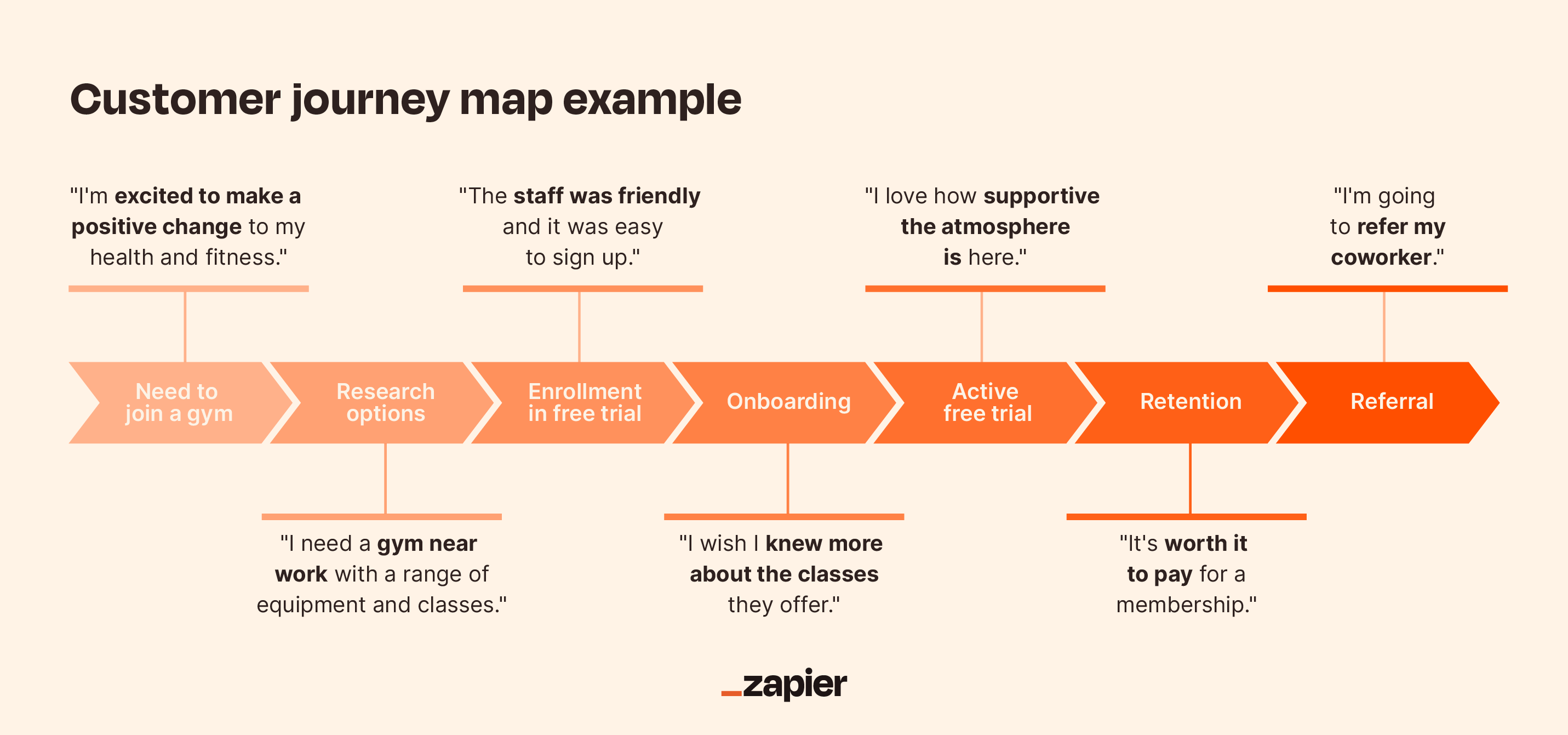
In this example, a SaaS company similar to Zapier has filled out this general customer journey map and documented the customer's journey step by step.
Awareness: The customer has identified the problem as efficiency in their processes. They're asking questions about potential solutions—and as a result, may see targeted ads or social posts based on their searches offering a solution.
Consideration: The customer is doing their research and comparing options. They're comparing features between similar products and reading case studies.
Intent and onboarding: Here's where the rubber meets the road. The customer is taking the solution for a test drive and may even have a free full-access trial.
Conversion: The customer is now ready to purchase. They may have a few final questions about ROI and price, but value has been established.
Expansion and advocacy: Finally, the customer has developed such an appreciation that they're ready to advocate—or even increase the number of services they purchase from you.
While your stages may look a little different, the key here is to understand what questions your customers ask at each stage and how to answer them.
Day in the life customer mapping example

In this example, a company that sells workout equipment has filled out a day-in-the-life customer journey map for one of their personas. This persona is dedicated to her training and always looking for a new tool, gadget, program, or supplement to increase her performance.
This journey is broken down into stages of the workout:
Pre-workout: The customer, Jane, takes her supplements and evaluates her stack. She might purchase additional supplements.
Warm-up: Jane uses tools to help her warm up, including resistance bands. She would likely purchase additional tools to assist with this stage.
Heavy lifting: Jane goes from her warm-up to the weight rack. We can infer that she probably has a gym membership.
Cardio: Jane is likely to explore other cardio options and might buy more equipment to support these endeavors. This could include a heart rate monitor, a jumping rope, or a new bike.
Cooldown: This is similar to the first stage but could include additional purchases like a sweat towel or a moisture-wicking top.
Each of these stages in the day-in-the-life journey offers a new opportunity to identify and meet a customer need.
Customer support journey mapping example

In this example, a customer goes through the support system process, interacting with both human support representatives and the automated systems that assist them. The whole process takes less than 20 minutes—but analyzing it can offer significant insights into how to better help and retain customers.
Submit ticket: The first stage begins when the customer experiences an issue and submits a ticket. This occurs automatically using a chat or form submission system—so it's important to make sure those systems are working correctly.
Submit additional data: An automated system typically follows up by asking some additional questions about the issue before transferring the customer to a support representative.
Chat with support: This is when a human steps in to resolve any remaining issues that the automated system can't solve. This transition should be as seamless as possible for the best CX.
Confirm issue is resolved: Did you resolve the issue for which the customer submitted the ticket? Failing to confirm this can be the difference between keeping or losing a customer.
Submit follow-up survey: Finally, the last stage is for the customer to submit their feedback on the support process so that your CX team can learn more about how to better help future customers.
This process looks much different than the first two since it focuses on internal responses to existing users or buyers, but optimizing your support processes for current customers is just as crucial as supporting future customers.
Customer journey mapping best practices
Everything we've covered up to this point will only get you as far as a basic customer journey map. Once you've got your mapping structure down, you'll want to take steps to continually improve your map's effectiveness. Here are a few best practices to keep in mind.
Automate customer data collection
High-quality, premium experiences are defined by their high level of personalization, and that personalization is only possible if you have information about your customer. But manually collecting and organizing that information is time-consuming and near impossible to scale.
With Zapier, you can connect thousands of apps, including popular marketing and lead generation tools, to automate the entire experience. For example, when a new form submission comes in, Zapier can automatically add lead data to your CRM, enrich it with AI-generated insights, and add tags based on customer behaviors like emails opened or products purchased. At the same time, you can use AI to draft a personalized response and flag it for human follow-up, if needed. It's everything you need to give your teams the context they need to deliver more relevant, personalized customer experiences at scale. Here are a few pre-made worfklows to get you started.
Add new Unbounce form submissions to Pipedrive as deals
Add new Facebook Lead Ads leads as leads in Salesforce
Enrich new Typeform entries with ChatGPT and add a note in HubSpot
Zapier is the most connected AI orchestration platform—integrating with thousands of apps from partners like Google, Salesforce, and Microsoft. Use forms, data tables, and logic to build secure, automated, AI-powered systems for your business-critical workflows across your organization's technology stack. Learn more.
Survey your customers and customer teams
When designing touchpoints and determining where and how customers interact with your business, don't guess. Your existing customer base is a valuable resource you can tap for a firsthand customer perspective. A common approach to getting customers to participate in surveys and filling out feedback forms is by offering discounts and perks in exchange.
Talk to your customer-facing employees, too. The people who work directly with customers daily will have more accurate information about how to interact with them.
Tweak for B2B, B2C, and SaaS industries
The nature of the customer journey is different for SaaS, B2B, and B2C companies. For example, a B2B company's interactions with prospects might include in-person conferences, while a SaaS company's touchpoints will be mostly digital. A company that sells to consumers will need to think through individual people's daily experiences, whereas a company selling products designed for emergencies will need to think through crisis scenarios instead of day-to-day customer experiences.
Tweak your customer journey categories to fit your company, product, and industry. Using a generalized or poorly fitting customer journey map will result in vague and unhelpful interactions with your brand.
Create multiple maps for different journeys
When people refer to the customer journey, they're typically talking about the overarching journey from awareness to brand loyalty that we outlined above. But you can map any part of the customer journey and experience.
Do you target college students? Replace the five stages with four academic quarters and map their experience over the course of a year.
Is your product designed to be used in the car? Map the customer journey through each hour of a long road trip.
Zooming in to create detailed maps of different aspects of the customer journey will help you create even more specifically tailored customer experiences.
Benefits of customer journey mapping
In a world where there are multiple high-quality options for just about every product on the market, brands need to foster long-term relationships with their customers to prevent them from being poached by competitors who offer a better customer experience.
Here are the main benefits of the customer journey mapping process:
Touchpoint optimization: Once you've mapped out customer touchpoints—moments when a customer interacts with your brand, directly or indirectly—you can easily track and adjust them based on performance, giving your customer a better overall experience.
Enhanced customer experience insights: Customer journey mapping naturally reveals how customers think, feel, and behave throughout their journey. This enables you to uncover pain points, unmet needs, and hidden opportunities that aren't obvious from isolated data.
Improved product development: Thoughtful and intentional journey planning creates more opportunities for meaningful customer feedback, which gives businesses better information to improve their product.
Automate your customer journey mapping with Zapier
Customer journey mapping is only as powerful as the systems that support it. When teams rely on manual data gathering across scattered tools and siloed workflows, journey maps quickly lose their ability to guide real decisions.
Zapier streamlines customer journey mapping by orchestrating the data, insights, and actions that power every stage of the experience. Instead of stitching together dozens of touchpoints by hand, you can rely on automated, AI-driven workflows that keep your map accurate, responsive, and actionable.
With Zapier, you can:
Connect data from across your stack. Zapier connects with thousands of apps, meaning you can bring events, interactions, and behavioral signals from anywhere—your CRM, support platform, marketing automation tools, or product analytics—into a unified flow.
Trigger the right action at every moment. Set up automated workflows that intelligently move leads down the lead generation funnel and continue to nurture them well past their first purchase.
Enrich your journey map with AI insights. Use AI-powered steps to classify feedback, summarize conversations, identify patterns, or predict the next best action.
Keep your journey map continuously up to date. By automating data movement across systems, your customer journey maps adapt as customer behavior evolves—not just when someone has time for a refresh.
Build AI agents to support your customer journey. Zapier Agents can pull in your knowledge sources and take action autonomously across your entire tech stack. No matter how bespoke your customer journey, AI agents can adapt and act to keep folks moving through the funnel.
Related reading:
This article was originally published in May 2021 by Nick Djurovic. The most recent update, with contributions from Jessica Lau, was in December 2025.