We haven't exactly worked out all of AI's kinks yet. Just try asking ChatGPT to solve a basic math problem or tell you how many R's are in "strawberry." You'll get a different, probably unhinged, answer every time (yes, still). That infamous variability is fine for brainstorming and exploration, but it becomes a problem when you embed AI in real workflows where your team needs consistency and control.
In enterprise settings, predictability and clear outcomes matter just as much as generative capability. Salesforce executives recently acknowledged that their confidence in large language models had declined compared with a year ago, and the company would be shifting toward more predictable, rule-based automation inside its Agentforce product. In other words, deterministic AI is gaining traction.
Here's everything you need to know about deterministic AI, how it differs from non-deterministic AI systems, and how hybrid approaches can combine AI's ability to interpret complexity with workflow logic that ensures repeatable results.
Table of contents:
What is deterministic AI?
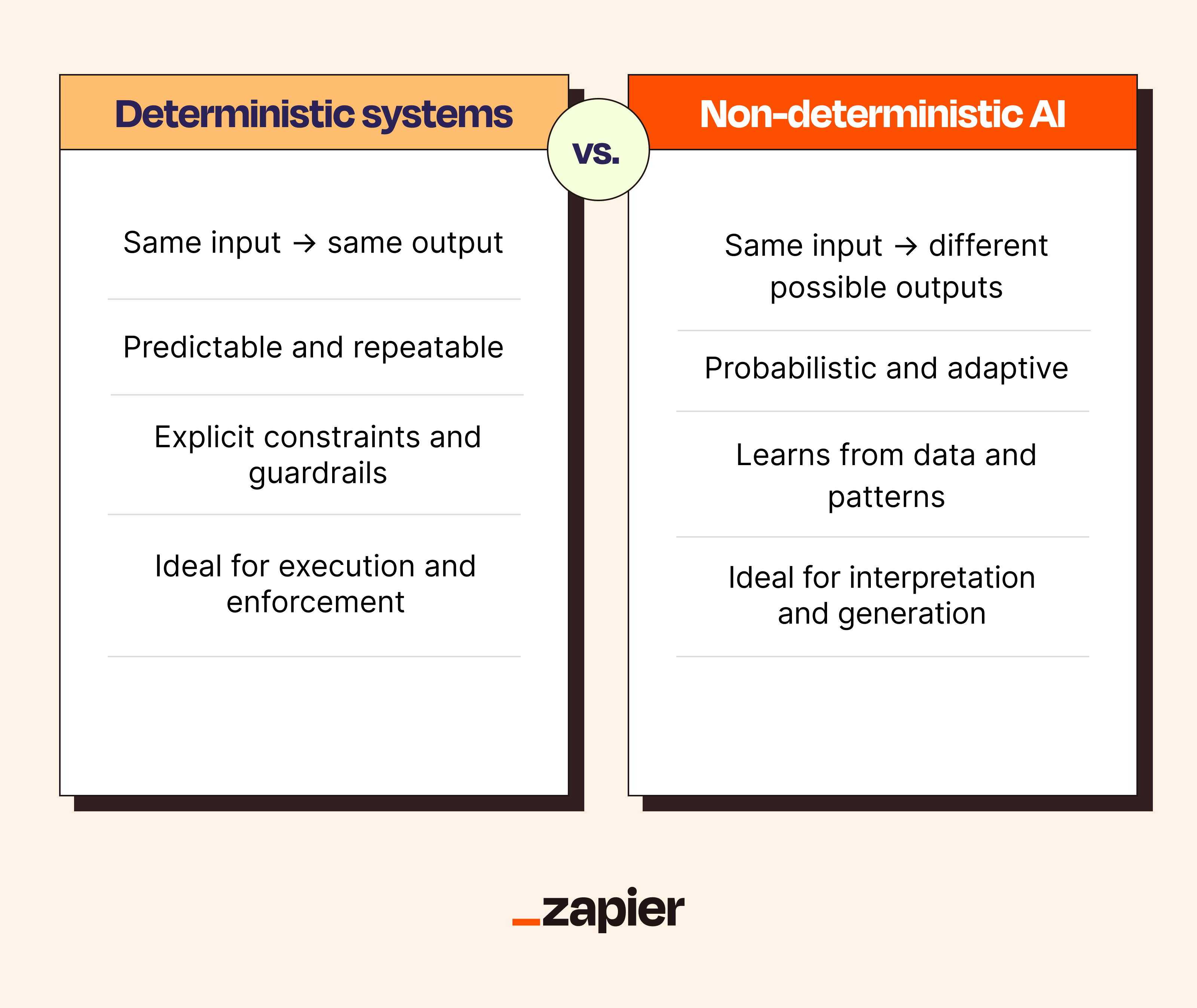
In technical terms, a system is deterministic if it produces the same output every time it receives the same input. Traditional automation fits this definition perfectly, since rules-based workflows and formulas all behave in predictable, repeatable ways.
AI, on the other hand—especially modern machine learning models—is usually probabilistic. It generates outputs based on likelihoods rather than fixed rules, which is why the same prompt will often produce different results.
Deterministic AI systems use AI models (like LLMs) that are probabilistic under the hood, but the overall system is deterministic. AI is deployed inside deterministic workflows, and those AI models may be configured to behave predictably (for example, by fixing model settings or tightly constraining how outputs are used). The same input leads to the same result every time.
That's why deterministic AI often looks a lot like automation; it is automation, just with AI embedded inside it. The difference is that instead of relying solely on human-authored rules ("if X, then Y"), these workflows rely on AI's ability to interpret language, classify data, or make judgments, then execute those decisions in a predictable way.
Zapier is designed for exactly this kind of setup. The platform provides the deterministic execution layer by connecting apps, enforcing logic, and coordinating actions, while allowing teams to incorporate AI wherever interpretation is needed. The result is AI-powered workflows that remain reliable and controlled in production.
Deterministic vs non-deterministic AI systems
A deterministic system produces the same output every time it receives the same input. When AI is involved, determinism usually comes from how the system is built: AI may help interpret information or make a judgment, but the surrounding workflow enforces consistent, repeatable execution.
For example, imagine an incoming customer message. An AI model might analyze the text to determine intent or urgency. That interpretation is then passed into a deterministic workflow—such as a Zapier automation—that routes the message, updates records, or triggers follow-up actions according to predefined rules. Given the same input, the workflow behaves the same way every time.
A non-deterministic AI system, on the other hand, produces outputs based on probabilities. The same input can lead to different results depending on context, sampling, or model behavior. These systems are best suited for cases where variation is acceptable, or even desirable.
For example, prompting an AI model to draft a response or brainstorm ideas will often produce different outputs each time. That flexibility is useful for generation and interpretation, but it's less suited to workflows that need consistent, production-ready outcomes.
When to use non-deterministic AI
Deterministic systems trade flexibility for control. They're less able to adapt to changing logic, and they can struggle with nuance, ambiguity, or unstructured data. They also require careful upfront design to cover edge cases.
When the problem you're solving is inherently ambiguous or open-ended, non-deterministic AI is usually the better fit. It's usually best to reach for non-deterministic AI when you need:
Pattern recognition across large or messy datasets
Natural language understanding
Classification, summarization, or extraction
Content generation or ideation
Systems that adapt as inputs and data change
In practice, many teams want the strengths of non-deterministic AI without giving up deterministic behavior—leading to a hybrid approach that combines both.
Read more: What is generative AI?
When to use deterministic systems (including deterministic AI)
Deterministic systems are a strong fit when consistency and control matter more than flexibility. They're built with guardrails to limit unexpected behavior, and they're easier to test, debug, and monitor.
They're especially useful for workflows that need to behave reliably in production, where every decision should be understandable, traceable, and repeatable. You'll want to lean toward deterministic systems when you need:
Fully consistent, repeatable outcomes
Policy or rule enforcement
Clear handoffs between systems
Decisions that can be reviewed or explained by humans
Production workflows with low tolerance for variability
In many of these scenarios, AI still plays an important role—but not as the final decision-maker. Instead, it's embedded inside an otherwise deterministic workflow, supporting execution rather than replacing it.
Non-deterministic AI is well-suited to the messy parts of work. It can interpret natural language, extract meaning from unstructured inputs, and make judgment calls when there isn't a single right answer. Deterministic workflows, by contrast, are designed for execution. Once a condition is met, the same action happens every time, predictably and reliably.
That's why most real-world systems combine both. In a deterministic AI workflow, non-deterministic AI is used for interpretation, while deterministic logic governs what happens next.
A simple example looks like this:
Input → AI interpretation → deterministic execution
This is where Zapier fits in as an AI orchestration layer. Zapier provides deterministic execution by connecting 8,000+ apps, enforcing rules, and coordinating actions, while allowing teams to incorporate AI tools where interpretation is needed. AI can classify an input, extract key details, or assess intent, but the workflow itself remains structured and controlled.
By keeping execution deterministic, teams can build workflows that are easier to test, monitor, and evolve over time. AI becomes one component in a larger system rather than a black box that directly drives outcomes. That separation also makes it easier to introduce AI gradually, enhancing specific steps without disrupting everything downstream.
Read more: Automation vs. AI: What's the difference?
How to implement deterministic AI
Your AI-supported work processes are at risk of chaos without a few guardrails—otherwise known as deterministic execution. After all, AI is all fun and games until your customer service chatbot starts hallucinating 100%-off discount codes.
Here's how to get started implementing deterministic AI in your business.
1. Define the trigger
First, identify the activity that kicks off the AI-powered workflow. It could be a new email, a form submission, a record update, or any other change that matters to your team. Having a precise trigger not only ensures the right data flows into the system but also frames the bounded context where you're applying AI.
2. Decide where in the workflow to use AI
Once you've defined the trigger, the next question is: where in the workflow should AI be used? This usually comes down to identifying points where the input needs interpretation.
AI by Zapier shines at turning unstructured or ambiguous data into structured signals. That might mean summarizing the body of an incoming email, classifying a support request by urgency, extracting key fields from a messy document, or scoring feedback for sentiment. By inserting an AI step at the right point, you're taking advantage of AI's strength without letting it decide the outcome on its own.
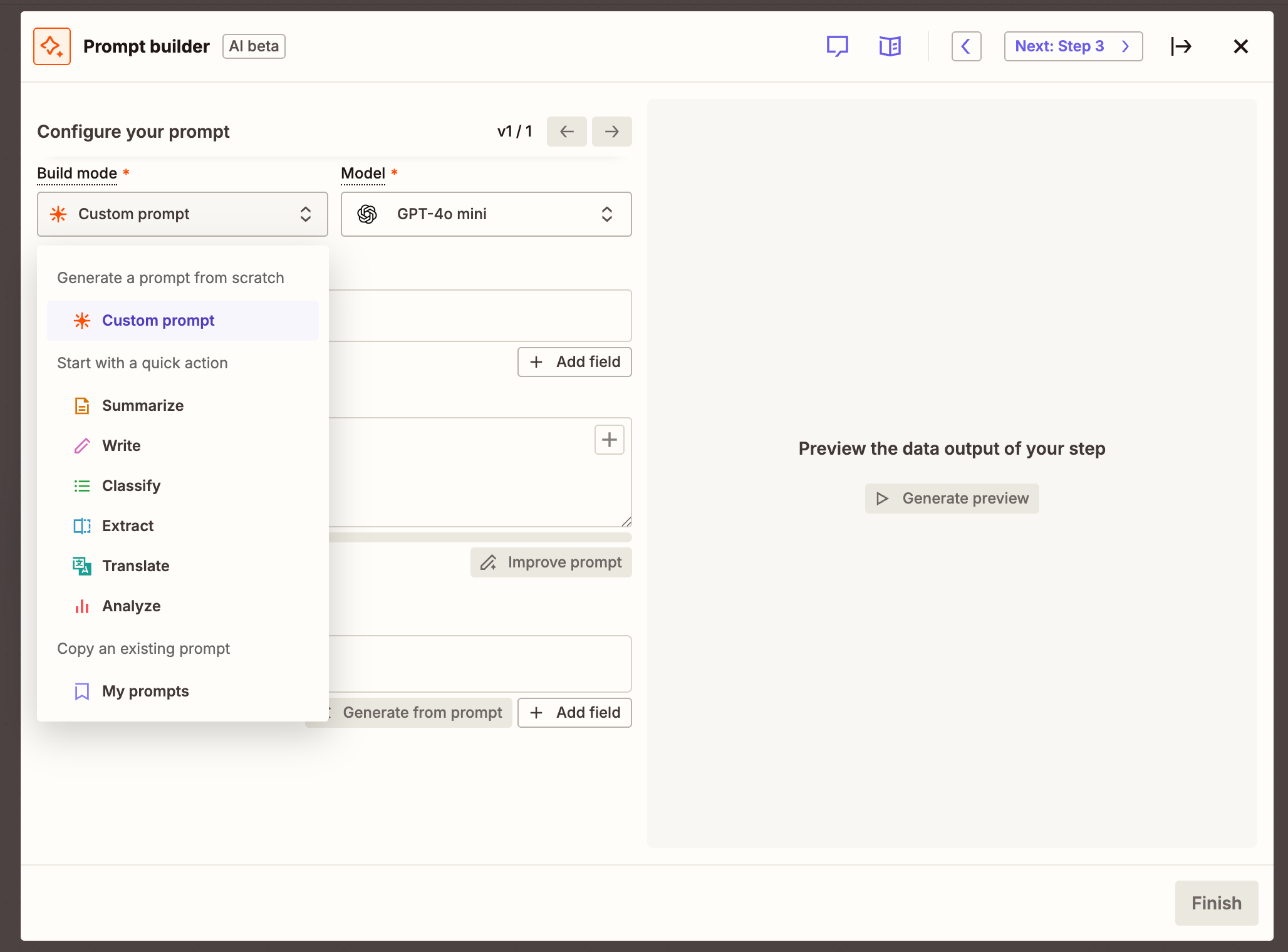
3. Create the deterministic decision layer
Once the AI has produced its output, it should feed directly into a deterministic decision layer. This is where predefined logic, rules, and operations take over. If the AI's output signals that an email contains high-priority language, the deterministic part of your system might route that to a specific team, update a status field, or trigger a notification—always the same way each time. The deterministic logic enforces consistency and ensures predictability in execution.
As you build out these hybrid workflows, it's helpful to think in terms of a loop: interpret → structure → enforce. The AI interprets unstructured or ambiguous inputs, you structure that interpretation into reliable signals, and then your deterministic logic enforces the outcomes you expect. Over time, this approach makes it easier to test and monitor your workflows because you always know how the non-AI components will behave once the AI output is fixed.
4. Iterate and scale
Finally, keep building on your deterministic AI systems. Zapier Copilot can generate ideas for workflows based on a natural language prompt, which helps you go from concept to implementation more quickly. This doesn't change the underlying hybrid architecture, but it does make it easier to prototype and refine the points where AI and deterministic logic intersect.
By defining clear triggers, using AI where interpretation matters, and keeping deterministic logic in charge of execution, you can implement systems that behave predictably in production while still benefiting from AI's ability to understand complexity.
Real-world deterministic AI examples
Here's how teams are combining non-deterministic AI with deterministic execution to build systems that are flexible where they need to be, and reliable where it counts.
Easy Aiz: Turning unstructured input into predictable content workflows
The team at Easy Aiz wanted a faster way to turn ideas into published content. Those ideas often started as unstructured inputs: voice notes shared in Slack, rough thoughts captured on the fly, or informal discussions that weren't ready for production. This is exactly the kind of scenario where non-deterministic AI is useful. AI interprets those inputs—transcribing voice notes, summarizing key points, and shaping them into structured drafts.
Then, once the content was structured, deterministic workflows took over. The same steps happened every time: content was routed to the right tools, formatted consistently, and published across predefined channels.
This hybrid setup allowed Easy Aiz to scale content production without sacrificing reliability. AI handled interpretation and generation, while deterministic automation ensured that each output moved through the workflow in a predictable way. The result was a system that saved significant time and delivered consistent results, even though the inputs were anything but consistent.
Portland Trail Blazers: Using AI to interpret feedback without losing control
The Portland Trail Blazers receive a high volume of guest feedback, much of it unstructured and time-sensitive. Messages can range from simple compliments to urgent service issues, and manually reviewing every submission slowed response times. This is where non-deterministic AI adds value by quickly interpreting free-form feedback, identifying themes, and assessing urgency.
The team used AI to analyze incoming messages and extract structured signals, such as sentiment or priority level, from otherwise inconsistent inputs. But those signals didn't directly trigger open-ended actions. Instead, they flowed into a deterministic workflow that governed what happened next.
Once feedback was categorized, predefined logic handled routing and follow-up. High-priority messages were escalated consistently. Lower-priority feedback was logged or routed appropriately. Every decision followed the same rules, regardless of how the original message was phrased.
This hybrid approach helped the team dramatically reduce review time while maintaining confidence in the system's behavior. AI handled interpretation at scale, while deterministic automation ensured that responses were predictable, reviewable, and aligned with internal processes.
Vendavo: Using AI insights inside structured sales workflows
The team at Vendavo wanted to move more quickly from inbound signals to outbound action without adding complexity or manual steps. Sales conversations and inquiries often arrive in unstructured forms, and understanding what a prospect needs (or how urgent a request is) can require interpretation rather than rigid rules.
Non-deterministic AI helped bridge that gap. They used AI to analyze incoming messages and surface insights, such as intent or context, that would be difficult to capture with predefined logic alone. This interpretive step turned free-form inputs into structured signals that the rest of the system could rely on.
From there, deterministic workflows governed execution. Once an input was categorized or enriched, the same actions followed every time: routing leads, triggering follow-ups, or updating systems of record. The downstream behavior was consistent and predictable, even though the inputs themselves varied.
This hybrid setup let Vendavo modernize its sales operations without introducing uncertainty into core workflows. AI added flexibility at the point of interpretation, while deterministic automation kept execution reliable and aligned with existing processes.
The future of deterministic AI
As AI systems become more capable, the conversation around deterministic AI is starting to shift. Early on, determinism was mostly about reliability and making sure systems didn't behave unpredictably in production. Increasingly, though, it's becoming about accountability.
We're already seeing this play out in more regulated and risk-sensitive environments, where organizations need to understand not just what happened, but why. Deterministic systems make it easier to trace decisions, audit outcomes, and align AI-powered workflows with internal policies. As AI adoption grows, the need for clarity is only expanding.
At the same time, AI itself is evolving. Reasoning models are improving, and teams are getting better at expressing intent through clearer prompts, better feedback loops, and higher-quality data. As that happens, the line between probabilistic reasoning and deterministic execution becomes more intentional. The question shifts from "Can we trust this output?" to "Who's accountable for how this decision was made?"
This shift is especially relevant as agentic AI workflows gain traction. Autonomous or semi-autonomous agents can explore, propose, and reason in non-deterministic ways, but most organizations still want outcomes to be enforced deterministically. The emerging pattern is one where agents discover and recommend, while deterministic systems decide and execute.
That execution layer is where Zapier shines. It gives teams a way to connect AI tools to the systems they already rely on, while keeping outcomes predictable and controlled. If you want to combine AI's ability to reason with automation you can trust, Zapier gives you a practical way to do both, without choosing one at the expense of the other.
Related reading: