Last week, I took a quick audit of the tech stack for my other business (what I do when I'm not writing content like this). And I found we had 12 different tools with built-in AI capabilities.
And look, I'm not above outsourcing my brain to robots. But I'm noticing all the narratives about artificial intelligence are centered around "doing more" with not as much consideration given to AI security. In fact, in a recent Zapier survey, over one-third of enterprise leaders said AI sprawl is increasing security and privacy risks for their business.
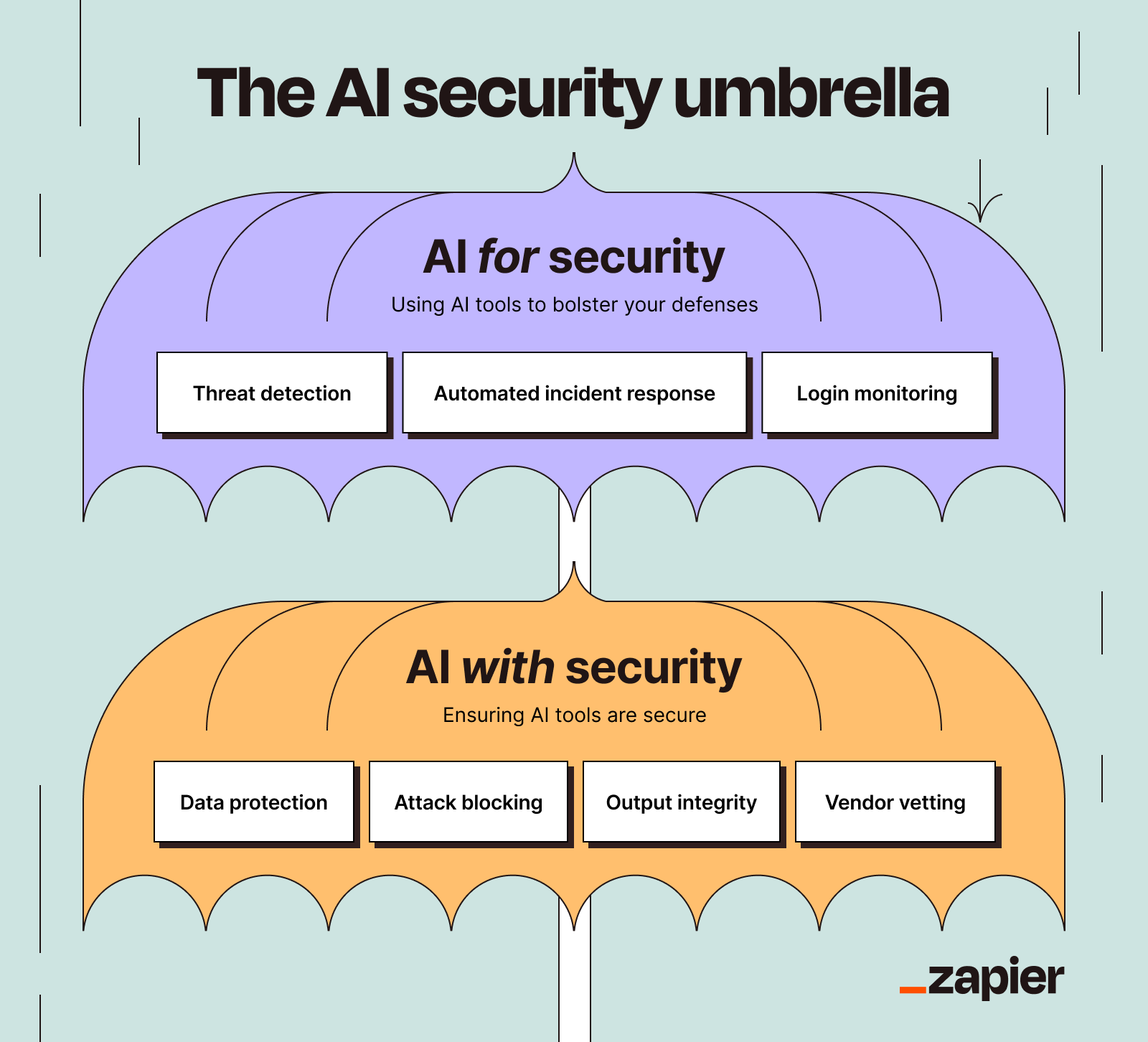
AI security is a two-sided story. On one hand, AI can offer tremendous cybersecurity benefits by offloading a lot of stress on your analysts. On the other, it introduces a new cyber attack surface that needs protection.
Table of contents:
What is AI security?
AI security is the protection of artificial intelligence systems from cyberattacks, unauthorized access, and misuse, while also leveraging AI to improve cybersecurity measures, such as anomaly detection and threat prediction.
The first aspect of AI security involves securing AI tools themselves from getting hacked, manipulated, or turned into weapons against you. This side of AI security includes protecting training data, locking down who can access the model, and making sure your employees aren't just casually uploading your entire customer database into ChatGPT because they wanted help writing a follow-up email. (Yes, people do this. People do this all the time.)
It also means defending against AI-specific threats like prompt injection (where attackers try to manipulate a model into ignoring instructions), data poisoning (where bad data corrupts behavior), and model theft or abuse through exposed APIs.
Then there's the second facet, which is using AI to make your company's cybersecurity better. Security teams increasingly rely on machine learning to spot patterns humans miss: unusual login behavior, suspicious network traffic, phishing attempts, and early indicators of compromise. AI can help triage alerts, prioritize incidents, and predict likely attack paths, particularly in environments where the volume of signals is overwhelming.
So when we talk about AI security, we're really talking about two sides of the same coin. On one side, AI is an incredible tool that can help you catch hackers, detect fraud, and automate security workflows. On the other side, AI itself is a shiny new attack surface that needs babysitting, rules, and oversight. It's like getting a guard dog that's also a puppy and might eat your couch if you're not watching.
Why AI security matters
Rapid AI adoption has amplified risks we already knew existed, while introducing risks we haven't adapted to yet:
Sensitive data processed at scale: AI often handles unfathomable amounts of customer information, financial records, proprietary business strategies, employee details, health data, purchase histories—you name it, AI is gobbling it up to "learn" and "improve." A breach or manipulated model here isn't a minor leak, but a full pipe burst with a massive blast radius.
High-value targets for attackers: Cybercriminals intentionally target this sensitive data because of its value. And if they manipulate the models themselves, they get control over powerful systems and tools used by many businesses today.
AI operates with minimal human oversight: Our "plug-and-play" trust in AI means a manipulated model can make costly, autonomous errors, and force poor decisions without us knowing. We're essentially blinded from the risk.
The data backs up security concerns and just how rushed the adoption of AI has become. According to our AI-resistance survey, 38% of enterprise leaders lack trust in AI vendor security, while 81% feel pressure from competitors to speed up AI adoption.
But here's the good news: this doesn't mean you should avoid AI. (That ship has sailed, my friend.) It's a reason to integrate it responsibly. An AI orchestration platform like Zapier can help here by standardizing how data flows between tools and by making it easier to build workflows with clear approvals, logging, and constraints, instead of one-off integrations that no one remembers how to audit.
Common AI vulnerabilities and security risks
If you want to protect your AI tools, you have to know what you're protecting them from. Here's how AI is keeping security professionals up at night, wondering if they should've gone into a less stressful field, like bomb disposal or lion taming.
Risk | Description | Best practices |
|---|---|---|
Data security risks | Training data (or prompts) can expose sensitive info; poisoned/unauthorized/low-quality data leads to unreliable outputs | - Anonymize data (remove PII) - Use DLP to scan/redact sensitive content - Pick tools with short retention - Ensure terms say your data isn't used for training |
Adversarial attacks | Attackers manipulate inputs or models (data poisoning, prompt injection, model stealing) to force bad decisions or leak data/IP | - Monitor for response drift - Pattern-match for exfiltration prompts - Use canary prompts to detect jailbreaks - Output allow lists + use-case whitelists |
Operational threats | Bugs/security holes, biased outputs, and model drift can cause failures even without an attacker | - Monitor for bias patterns - Test against diverse datasets regularly - Keep humans in the loop for high-stakes decisions |
Shadow AI risks | Employees use unapproved/public AI tools, creating governance gaps and potential data leakage | - Review login/SSO logs for usage - Run anonymous surveys to learn what/why - Set clear guidelines on approved tools |
Data security risks
AI models are trained on data, and lots of it. If that training data is poisoned, accessed without authorization, or is simply low-quality, the AI's outputs will be unreliable. You also expose your data anytime you run a prompt.
Imagine a customer service AI trained on a company's entire support ticket history, including account numbers, payment info, contact details, and past purchases.
This data, fed into AI to understand context, could be exposed in a breach. Worse, it could be used in a public model to further train the entire system for all users. So customers' private data could leak to others simply through the use of the right prompts.
Best practices to reduce risk: To mitigate this risk, anonymize the data so it's stripped of any personally identifiable information (PII) and use data loss prevention (DLP) controls to scan and redact sensitive content before it's shared. You can also choose platforms with specific short retention periods (those that purge data after a certain period) and ensure that their privacy terms specify that data isn't used for training models.
Adversarial attacks
AI cybersecurity attacks are where things get sneaky. Cybercriminals can manipulate inputs for learning models to deceive the AI. Here's what it could look like:
Data poisoning: Attackers can corrupt training data, causing the language model to learn incorrect information from the start. Although the AI may appear normal, its decisions are based on fundamentally flawed information, potentially leading to catastrophic outcomes like approving fraudulent transactions or denying legitimate customer requests.
Prompt injection: This is basically social engineering for AI. Clever inputs can trick the AI into bypassing its safety guidelines and security policies, causing it to expose confidential data or perform unauthorized actions. It's like hypnotizing a security guard into opening the vault.
Model stealing: Bad actors repeatedly query a learning model to reverse-engineer how it works, effectively stealing your proprietary AI tools. Industrial espionage, but make it algorithms.
Best practices to reduce risk: In these cases, detection is a good mitigation practice. Monitor for response drift and use pattern matching to flag exfiltration prompts. Use "canary prompts" (unique, secret strings of text designed to detect jailbreak attempts) to see if your model is being manipulated. Implement output allow lists so your AI can only respond in pre-approved, safe formats. And apply use-case whitelists that restrict what your AI tools can actually do. Basically, put your AI in a very controlled, very supervised sandbox and don't let it out unsupervised.
Operational threats
Adversarial attacks are when someone is actively trying to mess with your AI. But operational threats are the things that go wrong even when nobody's attacking you, and those problems can be just as dangerous as a hacker with a vendetta.
All software comes with security vulnerabilities, and AI is no exception. It can have bugs in the code or security holes that can be exploited. Since AI systems are often absurdly complex, those vulnerabilities can be really hard to find and fix. An attacker might exploit a bug to access the underlying system, steal data, or take control of the AI entirely. And because AI is supposed to be this magical, self-improving thing, companies sometimes forget that it still needs regular security patches and updates just like any other software.
AI models learn from data, and if that data is biased, the AI will be biased too. Flawed data or algorithms can intentionally create discriminatory, unfair outputs (disqualifying qualified job candidates or denying loan applications systemically). This isn't just a PR nightmare (although it definitely is that). It's a legal and ethical disaster, and the damage to your brand can be irreparable.
And then there's reliability. AI systems can drift over time, meaning their performance degrades or changes as they interact with new data. Something that worked perfectly six months ago might now be making terrible decisions. And because we trust these systems to run autonomously, we often don't catch the problem until there's a full-blown crisis.
Best practices to reduce risk: The fix here is constant vigilance. You should constantly monitor your AI models for bias. Look for patterns in their decisions, test them regularly against diverse datasets, and for high-stakes decisions, bring a human into the loop.
Shadow AI risks
Shadow AI is when your employees—those lovely, well-meaning people you work with—use unapproved or unsecured AI tools (like public LLMs) for work tasks.
The problem with shadow AI isn't that your employees are malicious. It's that they're human. They're overworked and looking for shortcuts, and they genuinely don't understand that feeding company data into public AI models is like shouting your secrets in a crowded mall and then being shocked when someone overhears. There's zero oversight, zero governance, and zero awareness of where that data goes or who can access it later. It's a data leak waiting to happen.
Best practices to reduce risk: Reduce shadow AI risks by regaining control. Review employee logins and SSO logs to see what exactly they're using. You can also (and this might sound wild) ask people what they're using. Send out an anonymous survey and make it clear you're not trying to get anyone in trouble (even if you're internally screaming) and that you just want to understand the gaps in your current tech stack that are driving people to find their own solutions. Uncovering this info, combined with clear guidelines on approved tools, helps control AI use.
AI security best practices
Stay prepared and protect your business with these sensible AI data security best practices. They'll keep you from becoming the cautionary tale in next year's cybersecurity horror story anthology.
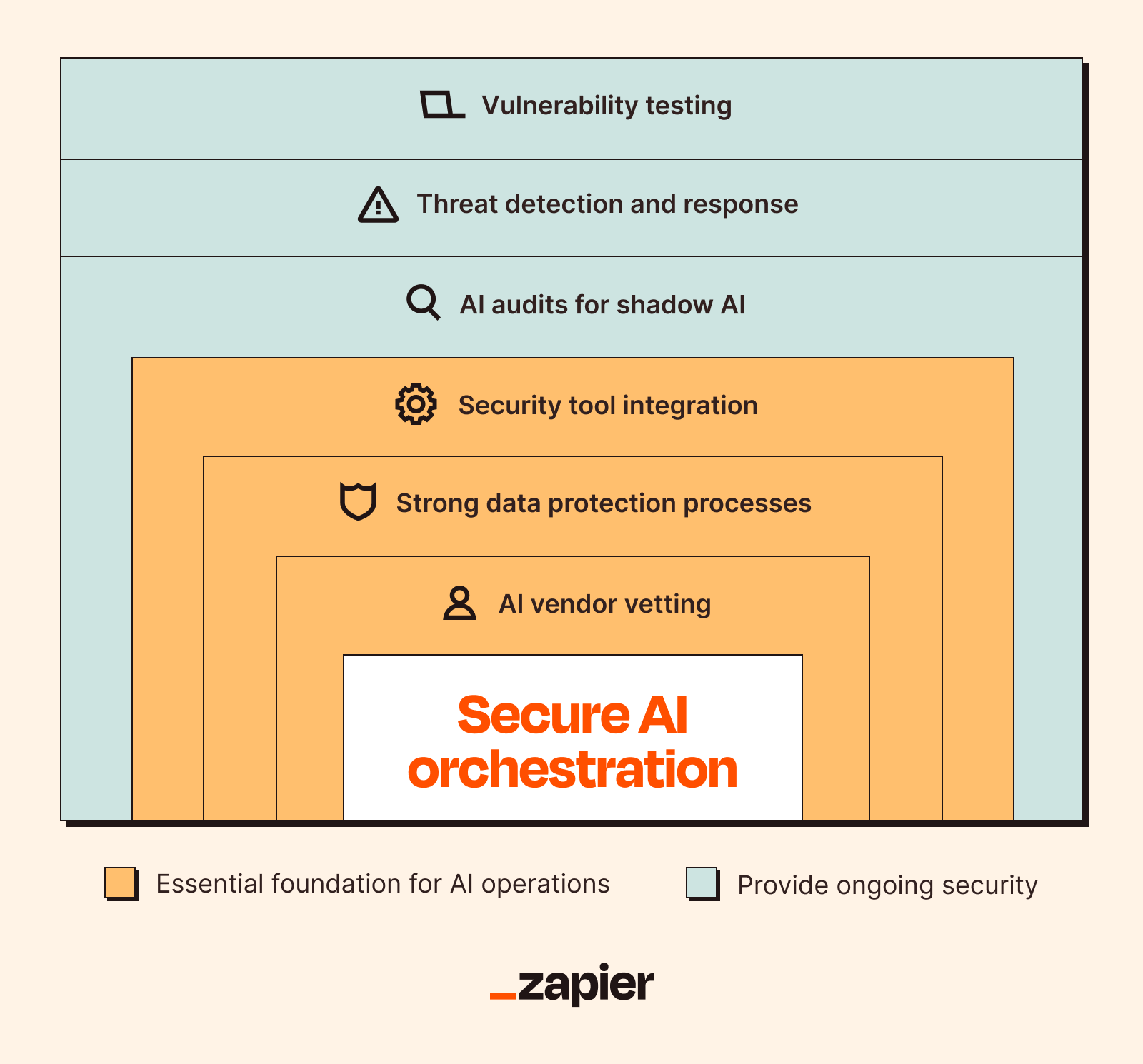
Choose a secure AI orchestration platform: An orchestration platform offers a great line of defense. Tools like Zapier sit between your AI apps and core systems (like your CRM, ERP, communications tools, etc). It's an easy way to automate and use AI without giving the tool direct access to your sensitive data.
Implement strong data protection processes: Anonymize or pseudonymize sensitive data before using it in AI workflows. Then, establish clear data governance policies with rules for users on what they can (and can't) feed into AI models. And don't forget to follow zero-trust security (by verifying access to every AI tool).
Carefully vet AI vendors: Before you adopt any new AI platform or service, do your homework. What are their data privacy and retention policies? Do they have security certifications like SOC 2? Is the model public or private? Do they have a bug bounty program or a responsible disclosure process? Are they transparent about their security practices, or do they get weird and evasive when you ask questions?
Integrate AI with existing security tools: Your AI shouldn't exist in a vacuum. So use AI-powered security by connecting it to your cybersecurity tools like endpoint protection software, identity and access management (IAM) systems, and security information and event management (SIEM) platforms. Use AI to track network and user activity, analyze behaviors, then auto-alert the security operations center (SOC) when something looks fishy. The more data your AI has access to (in a controlled, monitored way), the better it can identify patterns and spot threats.
Perform regular AI tool audits: Review your AI usage on a regular basis—monthly or quarterly, depending on how many tools you're using and how critical they are. Check for shadow AI that's cropped up since your last audit and make sure all your AI tools still comply with your company policies and any relevant regulations.
Leverage AI for threat detection and response: This is where AI becomes your friend instead of a liability. Use AI-powered security tools to monitor your network for anomalies, and automatically initiate responses like blocking a suspicious IP address or isolating a corrupted endpoint.
Regularly test models for AI security vulnerabilities: Most companies just deploy an AI model and leave it running forever, assuming it's fine. (STOP DOING THIS.) Your AI models need regular check-ups just like any other critical system. Audit for new vulnerabilities, biases, and performance drift to ensure they remain accurate and secure.
Orchestrate AI securely with Zapier
The promise of AI providing effortless automation and nearly instant insights is powerful. But without a secure foundation curbing irresponsible AI use, you risk exacerbating security issues—adding new vulnerabilities that could result in data privacy issues.
Zapier IT automation makes securing these workflows straightforward. You can orchestrate AI safely without a massive security overhaul, connecting AI tools to the rest of your tech stacks in minutes. It provides the buffer you need, with enterprise-grade security and compliance built in, having already vetted all the available AI tools in its ecosystem, so you're not flying blind trying to figure out which vendors are trustworthy.
And because Zapier focuses on AI security as a core part of its offering, you can actually sleep at night instead of lying awake wondering if your chatbot is going to leak customer data to a guy who operates out of a basement in Moldova.
Related reading: