I'm sure you've felt overwhelmed by the sheer volume of data your business generates: spreadsheets that stretch into eternity, dashboards that make your eyes glaze over, and the nagging sense that the numbers are painting a picture you can't quite make out.
That's where AI analytics can help. Instead of manually sifting through 10,000 rows of sales data with a highlighter and a stress headache, you can use AI to scan all that data in seconds, find patterns you'd otherwise miss, and get actual actionable insights.
In this guide, I'll break down what AI analytics is, how it works, and why it's so handy for any company that deals with numbers.
Table of contents:
What is AI analytics?
AI analytics is the use of artificial intelligence to automatically process, analyze, and extract insights from data. You can think of it as being akin to giving your data a brain—one that can learn, adapt, and even predict future outcomes.
What makes AI analytics different from traditional analytics is that traditional analytics requires you to know what questions to ask. You have to set up your queries, define your parameters, and tell the system exactly what you're looking for. It's like being a detective, but you have to know who committed the murder before you can start investigating.
AI analytics, on the other hand, is more exploratory. It can discover patterns and trends without you having to explicitly tell it what to look for. For example, instead of spending hours sifting through sales reports to figure out why revenue dipped last quarter, an AI-powered orchestration system could analyze customer behavior, market conditions, and operational factors to pinpoint the issue and suggest solutions all in a fraction of the time.
Key components of AI analytics
Most AI analytics tools rely on a few core technologies. Understanding them won't just help you appreciate what's happening behind the scenes, but it'll also impress people at parties. (Assuming you go to the kind of parties where people discuss vaguely intimidating tech jargon, which, if you're reading this article, you probably do.)
Machine learning (ML): ML algorithms automatically scan your data for patterns and trends, build predictive models, and improve over time through feedback loops. It's what enables AI to forecast customer churn, identify shifts in consumer preferences, or predict which leads are most likely to convert.
Natural language processing (NLP): A lot of valuable information exists in unstructured formats—customer reviews, social media posts, support tickets, etc. NLP allows AI systems to understand and interpret this kind of text data, extracting meaning and sentiment from language that wasn't specifically formatted for computer analysis.
Large language models (LLM): LLMs are advanced NLP systems trained on huge amounts of text. They can summarize dashboards, answer plain-language questions about your data, or explain what's driving a spike in signups in terms your stakeholders can understand.
Deep learning: This is a subset of machine learning that's especially good at handling complex, high-dimensional data like images, video, audio, or sensor inputs. Deep learning is what enables AI to look at a photo and tell you what's in it, analyze hours of surveillance footage to detect unusual activity, or process data from thousands of IoT sensors to predict equipment failures.
Data integration: Data integration is what allows AI systems to connect to all your different data sources—databases, APIs, cloud storage, wherever. Modern AI analytics platforms often feature "tool use" capabilities, meaning they can reach out and grab data from wherever it lives, without you having to manually export and import and reformat everything.
Types of AI analytics
Let's talk about the different types of AI analytics because—surprise!—there isn't just one way to analyze data with AI. There are actually several distinct approaches, each designed to answer different questions and solve different problems.
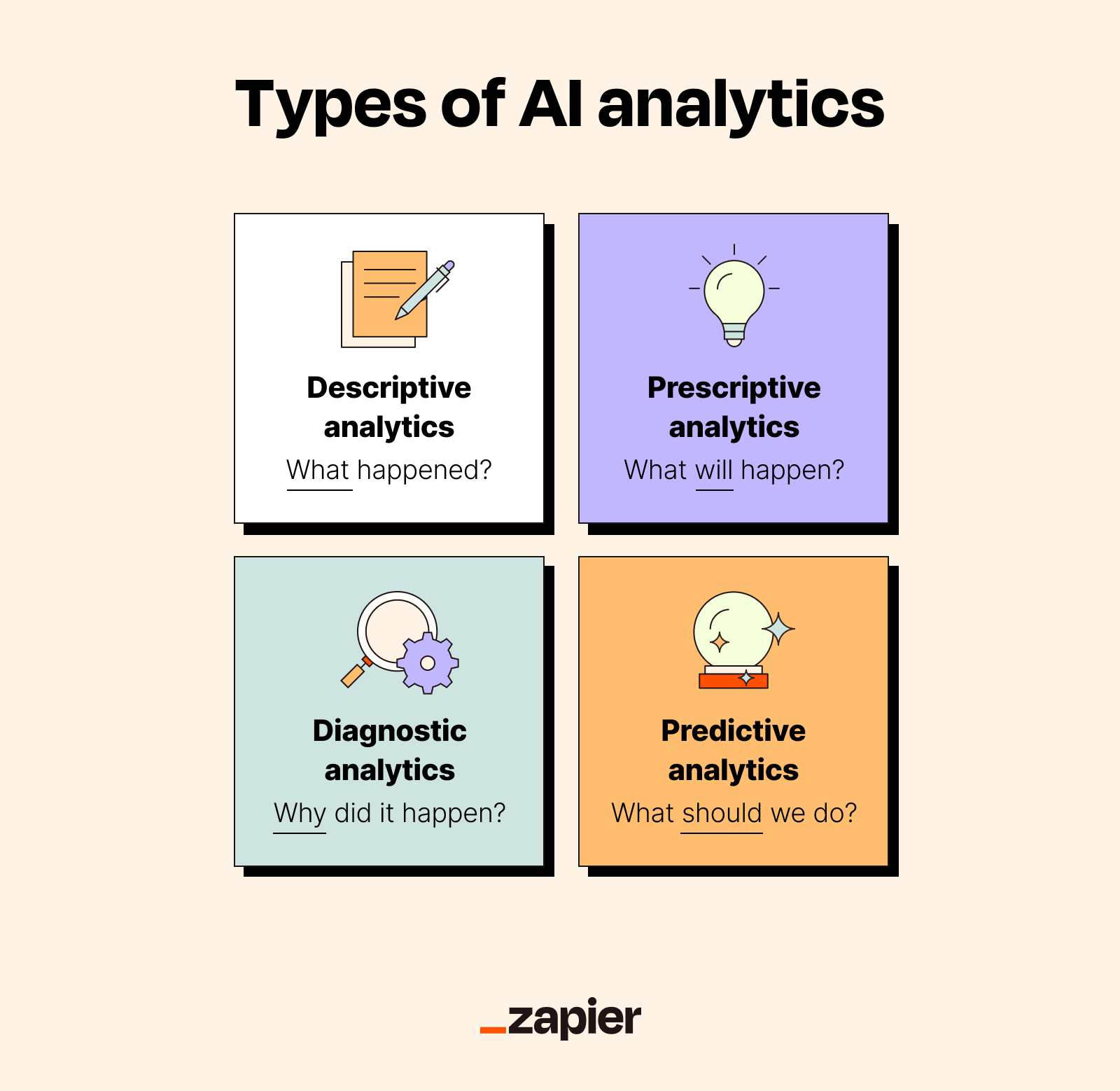
Descriptive analytics automates data aggregation and visualization, producing dashboards and reports with your historical data. Descriptive analytics tells you what's already happened, which might sound pointless, but is actually the foundation for everything else. You can't figure out where you're going if you don't know where you've been, you know?
Diagnostic analytics picks up where descriptive analytics ends, going further by unearthing the "why" behind a trend. Instead of just telling you that manufacturing output dropped last quarter, it digs into the drivers. The AI can analyze production logs, weather conditions, supplier records, and machine sensor data simultaneously to uncover variables, anomalies, and causal links that you'd never spot on your own.
Predictive analytics can tell you which customers are likely to churn, which leads are most likely to convert, when equipment is likely to fail, or how much inventory you'll need three months from now. It works by identifying patterns in past behavior and projecting them forward, adjusting for new information as it becomes available.
Prescriptive analytics doesn't tell you what happened, why it happened, or what's going to happen—it tells you what you should do about it. Using optimization, simulation, and reinforcement learning, it can evaluate multiple scenarios and recommend the best course of action. For example, a logistics company might use prescriptive analytics to determine optimal delivery routes based on traffic patterns, fuel costs, delivery windows, and driver schedules.
How AI analytics works
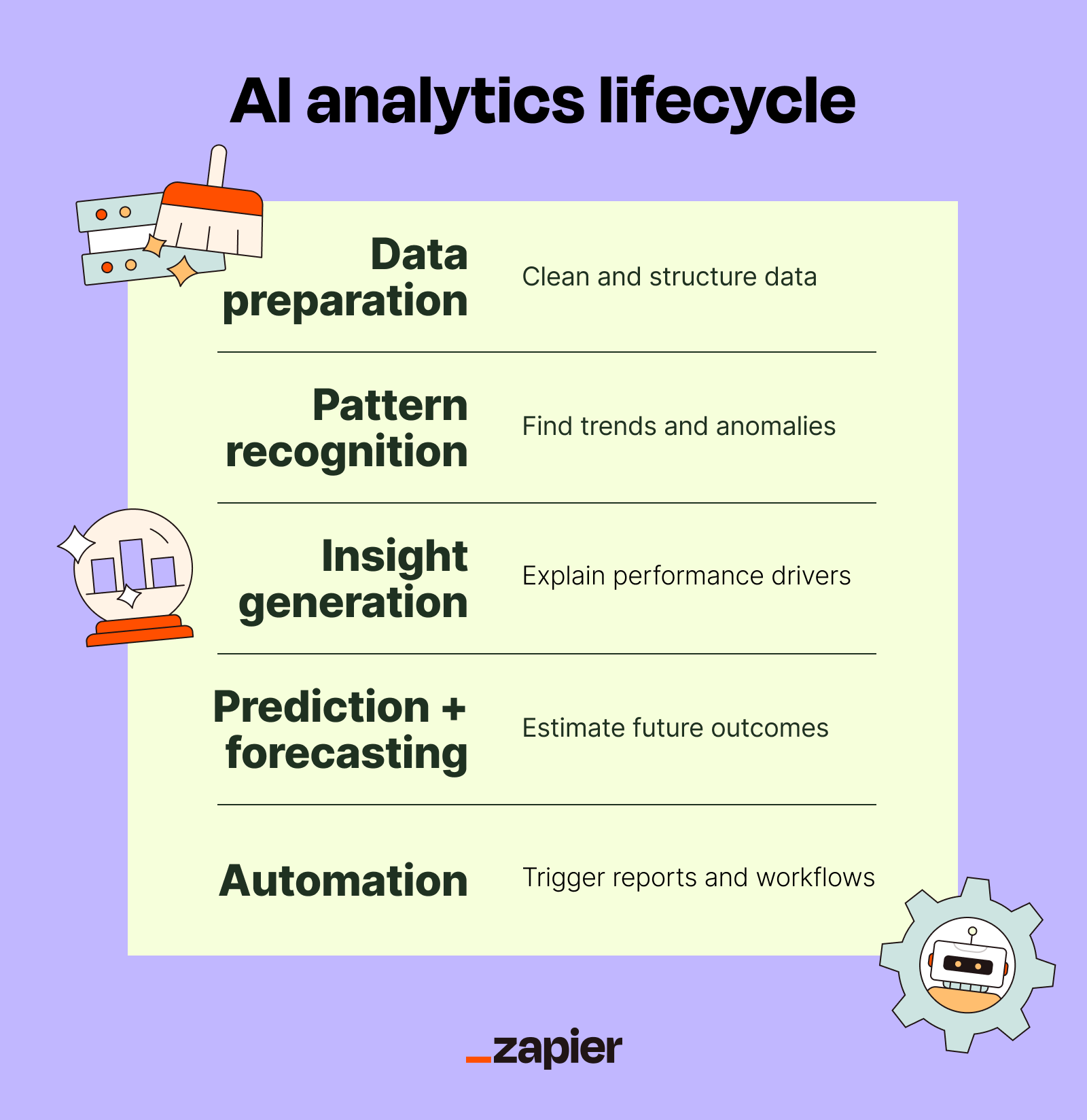
At a high level, AI analytics follows a repeatable pattern: clean up your data, look for patterns, turn those patterns into insights, and then use those insights to drive decisions and automation:
Data preparation: AI systems automatically gather, clean, and structure data from various sources, fixing inconsistencies, removing duplicates, filling in gaps, and getting everything ready for analysis. This rescues you from the kind of manual preprocessing that converts hours into dust and humans into husks.
Pattern recognition: Once the data is prepped, machine learning algorithms analyze it to identify trends, relationships, clusters, and anomalies that humans would probably miss. The AI can detect subtle correlations, spot emerging patterns, identify outliers, and risks. See also: post hoc clairvoyance.
Insight generation: Of course, insights indecipherable are insights squandered. Using NLP and LLMs, AI translates complex statistical findings into summaries and visualizations, explaining what's driving performance shifts in language that makes sense to business stakeholders, not just data scientists.
Prediction and forecasting: Once the system understands historical patterns, it can project future trends and run "what-if" scenarios to estimate the impact of different decisions. This allows you to make business decisions before circumstances shove you into them.
Automation: AI analytics can feed into your existing systems so actions happen automatically, like:
Creating follow-up tasks when a high-intent lead crosses a certain score
Flagging an account for outreach when churn risk jumps above a threshold
Kicking off an incident workflow when system performance drops below an agreed SLA
Zapier can help get data into the right place, in the right shape, and to the right people, without a bunch of manual exporting, cleaning, and forwarding. You can automatically pull data from the tools you already use, standardize it, and route it to wherever you analyze it (a spreadsheet, database, BI tool, or even a Slack channel), then push the resulting insights into action via alerts, tickets, and follow-ups.
If you don't want to wire all of that together from scratch, use a Zapier AI workflow template to jump-start the whole flow. Start with templates to centralize and analyze customer feedback across channels, or turn meeting data into coaching insights, then customize them for your own data and tools.
AI analytics use cases
AI analytics shows up anywhere you've got more data than hours in the day, which, for most teams, is…everywhere. Here are a few of the most common (and useful) ways I see it put to work.
Sales and marketing
In sales and marketing (or RevOps), timing is everything, and AI analytics helps businesses stay ahead by predicting customer behavior and optimizing strategies in real time.
Predictive lead scoring uses historical deal data to predict which new leads are most likely to convert, then automatically flags them as high-priority in your CRM.
Customer segmentation clusters customers by behavior—like product usage, plan type, or engagement—and tailors campaigns instead of blasting the same message to everyone.
Churn prediction spots patterns in logins, support tickets, and billing data that usually show up right before a customer leaves, so your team can proactively reach out. A SaaS company, for instance, might use AI to detect declining usage patterns and trigger automated re-engagement emails or discounts.
With Zapier, you can connect those AI-driven insights to your CRM, email platform, advertising tools, or whatever other systems you use. For example, when the AI identifies a high-priority lead or an at-risk customer, Zapier can automatically update their record in Salesforce, trigger a personalized email sequence, and add them to a retargeting campaign. You can build these workflows from scratch or start with a template to hit the ground running.
Automate your HubSpot quote approval workflow to close deals faster and kick up your sales efficiency.
Supply chain
Supply chains are stupidly complex. They're massive global networks with thousands of moving parts—suppliers, manufacturers, distributors, logistics providers, retailers—all of which have to coordinate perfectly for products to end up where they need to be when they need to be there. It's honestly miraculous that anything ever arrives on time. AI analytics helps tame the chaos by improving efficiency and reducing risk across the entire chain.
Demand forecasting predicts future demand based on seasonality, historical sales, and external signals (like promotions or regional trends). A grocery chain could use this to optimize inventory levels, minimizing waste while ensuring popular items are always in stock.
Exception management flags anomalies in delivery times, order volumes, or supplier performance so humans can step in when needed.
Predictive maintenance can anticipate equipment breakdowns and failures before they happen. For example, a manufacturer might use sensor data to predict when a machine needs servicing, scheduling repairs during off-peak hours to avoid downtime.
With Zapier, you can integrate AI-driven supply chain insights into your communication and operational tools. When the AI detects that a shipment is likely to be delayed, for instance, Zapier can automatically send alerts to the relevant teams via Slack or Microsoft Teams. Or when inventory levels for a critical component drop below the AI-predicted threshold, Zapier can trigger a purchase order or notify the procurement team.
Finance
Precision and speed are paramount in finance—there's a reason trading firms spend millions of dollars to lay dedicated high-speed cables directly to data sources and locate their servers as close as physically possible to exchanges—and AI analytics is one way of delivering both.
Anomaly detection monitors transactions in real time. AI isn't quite at the level of the precogs from "Minority Report," but it can monitor activity streams to flag suspicious activity and prevent fraud. For example, an AI system might detect unusual spending patterns and temporarily freeze an account until the owner verifies the activity.
Credit risk modeling: Lenders rely on AI to assess creditworthiness more accurately by analyzing alternative data sources, such as social media activity or utility payments. This opens up lending opportunities for underserved populations while minimizing risk.
Portfolio optimization: Investment firms use AI to simulate different scenarios and recommend asset allocations that strike the best balance between maximizing returns and minimizing volatility. You might think this sounds like having a personal financial advisor who works 24/7, but it's really more than that—it's like having thousands of them you can spin up at a moment's notice, each one dedicated to gaming out a particular future and reporting its results.
Zapier can help even out these processes by connecting AI analytics outputs to compliance software, dashboards, or even mobile apps, giving the relevant stakeholders access to the latest insights.
IT
Finally, let's talk about IT, a field in which AI analytics can help keep systems running smoothly by identifying problems early, bringing them to your attention, and helping you plan a solution:
System performance monitoring: AI continuously monitors servers, networks, and applications, identifying bottlenecks or potential failures before they escalate. For example, an enterprise IT team might use AI to detect abnormal CPU spikes and allocate additional resources automatically.
Capacity planning: By analyzing usage trends, AI helps IT departments plan for future growth, ensuring they have enough bandwidth, storage, and computing power to meet demand.
Cybersecurity detection: AI excels at spotting threats that traditional security tools might miss, such as subtle changes in user behavior or network traffic patterns. For instance, an AI system could detect a phishing attempt disguised as a legitimate login and block it before any damage occurs.
Again, Zapier can tie all of this together by triggering automated responses. Zapier workflows can send alerts to IT staff or isolate compromised devices based on AI-driven insights. Check out this template of a ticket incident management automation for some inspiration on how you can similarly overhaul your own procedures.
Streamline incident response communication by kicking off the process and alerting your team.
Power your AI analytics with Zapier
AI analytics can revolutionize the way you work with data, but it works best when you can connect insights to actual action. With Zapier Agents, you can streamline the process of ingesting, transforming, and processing data.
Use Zapier Copilot to build agents with natural language, and they'll work in the background, tying together disparate data sources, handling tedious and error-prone formatting tasks, and surfacing new insights.
Related reading: