Language is complex. Chaotic. Ambiguous. From the moment we're born, we begin to process language—and it takes years of practice to get right. Try to learn a language later in life, or even just adapt to different local slang or idioms, and it can feel near impossible.
And somehow, the robots seem to have mastered it. Ask ChatGPT to wax poetic in the style of Maya Angelou, and it spits out multiple stanzas in a matter of seconds. Tell Jasper to write a tweet about Zapier, and it gives you a shippable social post.
So how exactly can AI understand language enough to talk back? It comes down to something called natural language processing (NLP), a process that enables AI applications to understand language by analyzing it, based on the billions of rules it's taught itself. Here's everything you need to know about NLP.
Table of contents:
What is natural language processing (NLP)?
Natural language processing (NLP) is a key part of artificial intelligence and computer science that enables machines to understand and infer meaning from human language, much like people can.
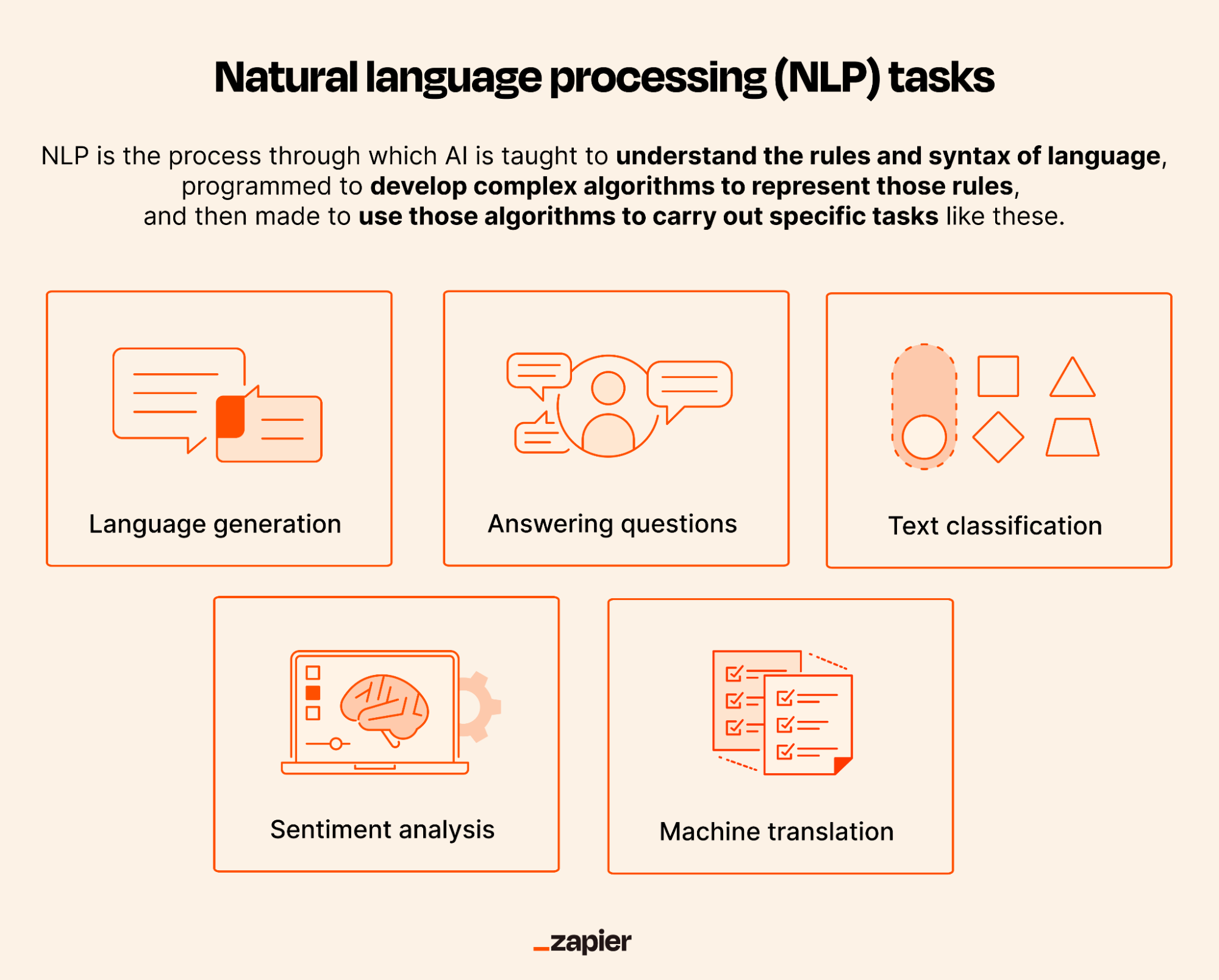
Essentially, NLP is the process through which AI is taught to understand the rules and syntax of language, programmed to develop complex algorithms to represent those rules, and then made to use those algorithms to carry out specific tasks. These tasks can include:
Language generation: AI apps generate new text based on given prompts or contexts, such as generating text for chatbots, virtual assistants, or even creative writing.
Answering questions: AI apps respond to users who've asked a question in natural language on a specific topic.
Sentiment analysis: AI apps analyze text to determine the sentiment or emotional tone of the writer, such as whether the text expresses a positive, negative, or neutral sentiment.
Text classification: AI classifies text into different categories or topics, such as categorizing news articles into politics, sports, or entertainment.
Machine translation: AI translates text from one language to another, such as from English to Spanish.
These are just a few key tasks that AI can do thanks to natural language processing. But how does AI even get to the stage of being able to do these things?
How does natural language processing work?
Before a machine can carry out any of these tasks, it first needs to understand how language works. This is done through a process called machine learning, where humans give it a massive amount of training data, or examples of language used in every conceivable context.
When we say massive, we mean massive. To put this into perspective, ChatGPT, OpenAI's chatbot, was fed over half a trillion words from books, text, articles, and data from the open web. That's equivalent to almost 75 Wikipedias.
But you don't just cram it full of data and hey, presto, your job is done. While words and sentences have meaning to humans, to computers they're just strings of text. For an AI to be able to comprehend them, human trainers have to label the data and help the computer learn how to understand language, what the rules and conventions are, and how to analyze it. This is done using natural language processing techniques.
Natural language processing and machine learning are both techniques used to create and inform larger language models.
Remember analyzing sentences in middle school English class? That was syntactic parsing: you'd have to isolate parts of a sentence and identify the subject, the object, the action verb, and so on.
It's exactly like that: the computer is taught to take a sentence or a word apart to understand how syntax works, the relationships between words, inferred meaning, and all sorts of other aspects of language. These techniques often involve:
Tokenization, where text is broken into smaller semantic units
Part-of-speech-tagging, where words are classified as nouns, verbs, adjectives, and other parts of speech
Stemming, where words are reduced to their base or root form
Dialogue management, where AI looks at stylistic patterns in conversations
When the computer has a grasp on these techniques, it can then transform its linguistic knowledge into deep learning algorithms. Then, in addition to being able to read and understand text, it can even write its own. This is what allows ChatGPT to generate text in response to a prompt. It takes what you said and replies based on the millions of language concepts it's learned. In most cases, this means predicting what text should follow your prompt in any given sentence by looking at examples of common patterns.
At this stage, human trainers usually fine-tune the model with feedback and reinforcement learning, so the AI generates the best response.
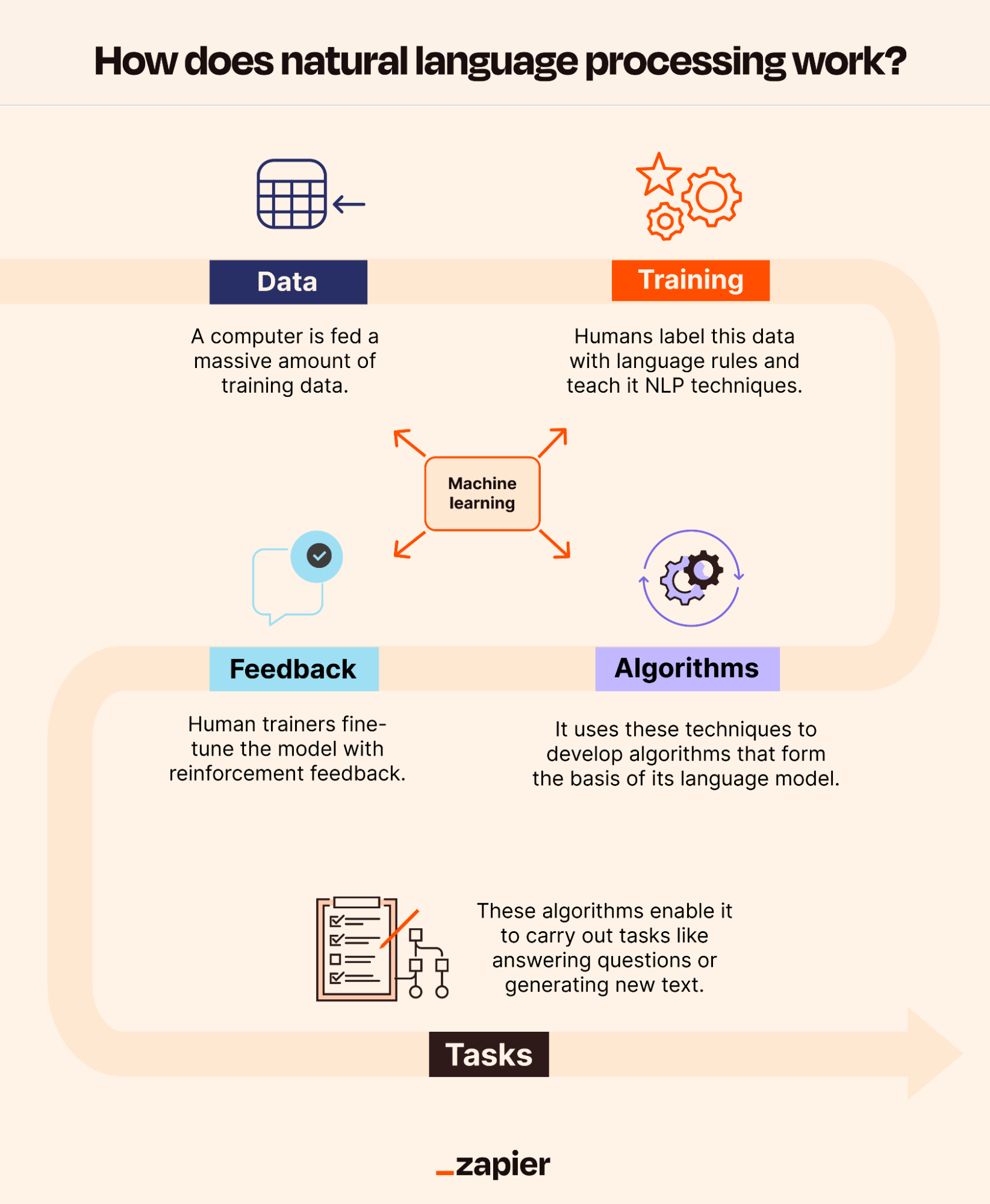
So, to recap how NLP works:
A computer is fed a massive amount of training data.
Humans label this data with language rules and teach it natural language processing techniques, like tokenization.
It then uses these techniques to develop deep learning algorithms that form the basis of its language model.
Human trainers fine-tune the model with reinforcement feedback. (Note: all four of these things are considered machine learning.)
These algorithms enable it to carry out tasks like answering questions or generating new text.
Keep in mind that, as much as the machines are being taught via training what is and isn't an apple, say, they're also developing their own internal system for recognizing it independent of however humans would.
NLP example: Natural language processing in AI chatbots
A lot of AI apps that generate text do so by predicting patterns in a human's prompt—then responding with the text that best matches the request. It's a natural language processing technique that allows them to predict the likelihood of a sequence of words (or tokens) in a sentence. Often it's successful—sometimes it's not.
But AI chatbots also analyze user intent, which is based on dialogue management (another natural language processing technique). This enables them to simulate a conversation by looking at other examples of dialogue in its training data—and mimic the same style.

In a nutshell, natural language processing is what enables chatbots to hold coherent conversations and understand user intent. But while chatbots can identify nuances in language—like sarcasm or slang words, most need to be prompted to replicate them.

Even though that's what I wanted, it still stung a little.
Related reading:








