I recently decided to fulfill my deepest desire: having scene transition music from "Seinfeld" play any time my front door opened. I figured it would be simple enough—just connect a door sensor and locally stored MP3s to a smart speaker, and Bob's your uncle, right?
Yeah, no. I massively underestimated the complexity of getting different bits of tech to talk to each other. By the time I (kind of) got it all to work, I'd lost the will to walk to the door, let alone laugh at the perfectly timed slap bass.
This same idea—connecting separate systems into a unified whole—is what businesses tackle daily, but on a much larger and more critical scale. Integration platform as a service (iPaaS) solutions enable organizations to seamlessly connect their applications, data, and workflows.
In this post, we'll explore what iPaaS is, how it works, and how it differs from other types of integration.
Table of contents:
What is iPaaS?
Integration platform as a service (iPaaS) is a cloud-based software service solution that lets organizations connect different applications, data sources, and legacy systems, whether they're in the cloud, on-premises, or in hybrid environments. It typically offers:
Pre-built connectors and low- or no-code tools to rapidly integrate popular SaaS applications.
Cloud-to-cloud focus, handling data flows between public-cloud services without on-premises dependencies.
Self-service for IT teams—but complex mappings may still require developer input.
Zapier, for example, lets you connect thousands of apps, providing a centralized solution for creating and managing your integrations—simplifying data integration, business process automation, and communication between otherwise unconnected apps.

What is enterprise iPaaS?
Enterprise iPaaS (also known as EiPaaS for reasons passing understanding) builds on the core capabilities of a standard iPaaS but adds the advanced features required for large organizations. It often features:
Enhanced security and governance including role-based access control, comprehensive audit trails, and compliance certifications (e.g., SOC 2, GDPR, HIPAA) to meet enterprise regulatory needs.
Centralized monitoring and analytics like real-time dashboards, SLA alerts, and policy enforcement across hundreds or thousands of integration flows.
Robust API management and B2B/EDI support, exposing integrations as managed APIs and handling industry-standard protocols like AS2, X12, and EDI.
Citizen-developer enablement lets you combine drag-and-drop builders with intelligent recommendations, so you can design and iterate on workflows without overloading IT.
Enterprise iPaaS solutions like Zapier scale with you so ICs, managers, leaders, and executives can all benefit from the technology.
How does iPaaS work?

The magic of iPaaS lies in how it abstracts away the complexity of integration. The iPaaS service provider handles all the unglamorous under-the-hood stuff like hardware upkeep, security patches, and whatever other wizardry happens in those mysterious server rooms.
In return, you get a no-code or low-code interface that lets you transform data, automate workflows, and create integrations between various apps. For example, you might use Zapier to orchestrate a workflow that kicks off when a new hire fills out your Typeform onboarding form. From there, it can run multiple workflows at once:
Add the new hire data to your HR database
Draft a personalized welcome message and send it in Slack
Schedule an orientation session in Google Calendar, complete with a Zoom link
The real heavy lifting is hidden in the background, leaving you free to not care how it's done.
But in case you're curious, here's how an iPaaS generally works:
Plug-and-play connectivity: With pre-built connectors and standard protocols, iPaaS links apps and data. These connectors standardize communication and make real-time data exchange less painful.
Data transformation and mapping: Let's say your lead gen app uses a data format best described as "WTF," and your CRM uses a format called "OMG." If you try to send "WTF" data to an app expecting "OMG" data, that's not going to work. iPaaS solutions have data transformation tools that reformat "WTF" into "OMG" so everything flows seamlessly.
Automated integrations: iPaaS synchronizes your apps automatically, eradicating data silos and giving your operations the streamlined efficiency they desperately need. On Zapier, for example, you can connect 8,000+ apps to each other using a visual builder.
Workflow orchestration: Beyond sending data around, iPaaS also orchestrates workflows. In other words, it can trigger multi-step processes, handle conditional logic, and help you automate a wide range of tasks. For example, Zapier can manage a full lead nurturing workflow: when a new lead is captured by a form, it can automatically enrich the data, evaluate the lead score with built-in logic paths, add it to your CRM, and notify the appropriate sales rep.
API management: In many iPaaS platforms, you can design, govern, and publish APIs from the same console you use to build integrations. This streamlines the creation of new services that might integrate with third-party partners or internal systems.
Centralized management and monitoring: Successful integration requires visibility. iPaaS provides dashboards that track performance metrics like latency, resource utilization, and integration efficiency. It also ensures your data is correctly routed and used, sparing you from hunting down issues in the dark.
No-code/low-code: Many iPaaS offerings provide low-code or no-code interfaces, which allow citizen integrators (AKA non-developers who maybe once successfully installed Chrome) to create and deploy new integrations through drag-and-drop interfaces and pre-built templates instead of extensive coding knowledge.
Real-time data flow: By connecting different systems, iPaaS facilitates real-time data exchange. This accelerates the flow of data, eliminates bottlenecks, and allows for faster and more informed decision-making.
Security and governance: Because not everything in life can be fun and games, iPaaS solutions also offer enterprise-grade security controls like encryption, user permissions, and secure data transit. Here's Zapier's security page as an example.
iPaaS vs. other integration solutions
Like dating apps, there are different integration solutions that serve different needs, and, also like dating apps, each one has its own special way of potentially disappointing you. Understanding how iPaaS fits in will help you decide if it's right for you.
iPaaS vs. ESB (enterprise service bus)
An ESB is a middleware that moves data between applications using a centralized "bus." It became popular in the early 2000s for connecting large, on-premise enterprise systems—think older ERP setups. ESBs usually require heavy coding, specialized skill sets, and complex deployments.
The main advantage of iPaaS over ESB is that it's cloud-based and far more accessible. You don't have to manage hardware or set up infrastructure. It's like ordering a pizza instead of erecting a brick oven in your backyard. That said, if you already have an ESB in place and purely local integrations, you might not see a strong reason to move away.

iPaaS vs. ETL (extract, transfer, and load)
ETL solutions are primarily used for data migration—pulling data out of one system (extract), converting it (transform), and sticking it into another (load). Often used in analytics or business intelligence settings, ETL is commonly associated with moving large batches of data from operational systems into data warehouses.
While iPaaS includes those capabilities—it can do ETL if you want it to—it's much broader. It's real time (not just batch), handles event-based triggers, orchestrates complex workflows, and is built for app-to-app communications, not just data warehousing.
ETL and iPaaS can often complement each other—you might use ETL for your data warehousing but rely on iPaaS to unify your day-to-day business operations across apps.

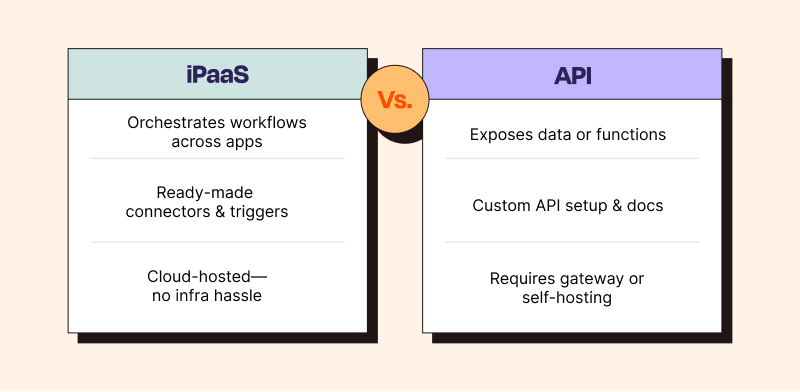
iPaaS vs. API
APIs (application programming interfaces) are like digital mediators that enable different software applications to talk to each other and exchange information. They define the methods, parameters, and data formats you can use to access certain features or retrieve data from an application or service. Think of APIs as the individual LEGO bricks of your software landscape.
By contrast, an iPaaS acts like a master builder, snapping those bricks together into complete workflows. Instead of hand-coding point‑to‑point integrations, you get:
Prebuilt connectors and visual mappings
Event-driven triggers
Hosted infrastructure
The main advantage of iPaaS over stitching together raw APIs is the speed and simplicity of creating end-to-end automations across apps. That said, if you only need to expose or consume a single service and want granular control over versioning or traffic, a standalone API might be the lighter-weight choice.
iPaaS vs RPA (robotic process automation)
RPA is a type of automation that uses bots to mimic human interactions with applications, such as clicking buttons, copying and pasting data, and filling out forms. It's ideal for automating repetitive tasks involving legacy systems or apps without APIs.
Both iPaaS and RPA aim to automate processes but tackle the challenge differently. RPA works at the user interface level, while iPaaS creates direct connections between systems. Think of it like that famous episode of "Seinfeld"—RPA is like navigating a strict, rule-heavy soup ordering process just to get a taste of the crab bisque, while iPaaS is like Elaine bypassing all the unnecessary steps by triumphantly getting her hands on the secret recipes. Next!

iPaaS vs. PaaS (platform as a service)
PaaS typically refers to a cloud offering that provides developers a place to build, test, and run custom applications. In a PaaS environment, you might spin up servers, configure storage, and deploy your own code. You can build your own integrations, sure—but that's not the main selling point of PaaS.
With iPaaS, integration is front and center, plus you don't have to be a pro developer to make it all work. iPaaS is less about building brand-new apps and more about letting your existing apps talk to each other and share data.

iPaaS vs. SaaS (software as a service)
SaaS is just fancy talk for renting ready-made software hosted by someone else instead of installing it on your own servers. Think: Slack, Salesforce, Airtable, or Google Workspace. SaaS is subscription-based, easy to deploy without local installation, and solves a specific problem.
iPaaS is a type of SaaS, but it specifically aims to integrate different systems, apps, and data streams. It doesn't replace other SaaS platforms—it's more like the central nervous system connecting them all.

iPaaS vs. hybrid integration platform
Hybrid integration platforms attempt to unite on-premises integration tools (like an ESB) with cloud services. The idea is that you might want some data flows to stay behind your corporate firewall but others to live out in the cloud.
Ultimately, "hybrid integration platform" is more of an umbrella term. iPaaS can be part of that puzzle, especially if your iPaaS vendor offers ways to plug securely into local data sources through specialized connectors.

Types of iPaaS integrations
Let's break down the different types of integrations like we're categorizing yoga poses—each one serves a purpose, even if some are more complicated than others.
Data integration
Data integration focuses on aggregating data from multiple systems into a single source of truth, ensuring accuracy and consistency across all apps. iPaaS automates real-time data synchronization so that, for instance, an update in your CRM is instantly reflected in your BI and marketing automation tools.
Example use case: A retailer consolidating customer purchase history from its eCommerce platform, in-store POS systems, and mobile app into a unified view for better analytics and personalization
API integration
API integration involves connecting two apps through their APIs so they can communicate with each other to share data or functionalities. It's like teaching your dog to bark in French so it can talk to a neighbor's poodle.
Example use case: Integrating a time-tracking app with a project management tool so that each time an employee logs hours, it reflects automatically in the project management system and can be billed accordingly
Service integration
Service integration is a broader term that includes orchestrating processes across multiple internal or external services—whether they're web services, microservices, or third-party service providers (such as payroll). iPaaS combines these services to create cohesive business workflows.
Example use case: A human resources information system that triggers a background check from a third-party provider whenever a new applicant is hired, then syncs those results back into the HRIS
System integration
System integration links different subsystems or software components within an organization's infrastructure, enabling them to function as a united system, even if they weren't initially designed to do so.
Example use case: A manufacturer connecting a legacy system that stores production data locally to a cloud-based ERP platform, giving operations staff real-time insights into inventory levels and production efficiency
Cloud integration
Cloud integration is the process of connecting multiple cloud environments or connecting local systems to the cloud so that everything can share data effortlessly. iPaaS is designed to handle those weird edge cases where you want to pull data from some relic from the Clinton administration and shove it into your shiny new data analytics SaaS tool.
Example use case: A company integrating its on-premises ERP system with a cloud-based data collection tool to ensure customer data synchronization across both platforms
B2B integration
We've talked a lot about internal application integration, but iPaaS can also streamline data flows and communication with external partners, suppliers, and customers. B2B integration takes the "hurry up and wait" out of business processes, allowing you to automate supply chain events, eCommerce transactions, data exchanges, and more.
Example use case: A manufacturer integrating its supply chain system with multiple parts suppliers' systems to automate order processing, inventory updates, and shipping notifications
Zapier as an iPaaS solution
While iPaaS might not make your smart speaker play funk-adjacent bass riffs, it can help your business run more smoothly, which is almost as good. Almost.
If you want to see how iPaaS can work in your own environment—connecting your apps, building automated systems, and even adding AI into the mix—try Zapier. This is the Zapier blog, so I'm obviously biased, but Zapier is the leader in user-friendly and powerful iPaaS, even for non-technical folks. And iPaas is only part of what Zapier can do—it's a complete AI orchestration platform that can automate all your mission-critical workflows.
Whether you're a business leader looking to streamline your operations or a larger organization seeking an enterprise-ready solution, Zapier provides the tools you need to orchestrate workflows that handle everything from accessible data synchronization to fully automated systems.
Related reading:
This article was originally published in September 2021 by Justin Pot. The most recent update, with contributions from Jessica Lau, was in August 2025.