There are plenty of ways to use GitHub: the website, the app, or the terminal. The terminal is the best way to sync local projects to a GitHub repository, and once you learn the basics, you'll be able to push local projects to remote GitHub repositories in seconds.
Here's a step-by-step guide on how to push to GitHub.
Table des matières:
What does it mean to push to GitHub?
Pushing to GitHub is a secure and convenient way to upload files to or update existing files in a remote GitHub repository.
For example, let's say you just created a new public repository for a project and you want to upload all your files to it. To do that, you would push your files to GitHub. Or maybe you're continually working on a project from a private GitHub repository for your company, and you want to upload the latest changes that you've made. That would also require you to push the changes to GitHub.
How to push to GitHub
Here's a step-by-step guide on how to push to GitHub. Note: Your Git terminal may look different depending on your operating system (I'm using Windows), but the steps are the same.
Before we continue, make sure you've installed and enabled Git on your local machine.
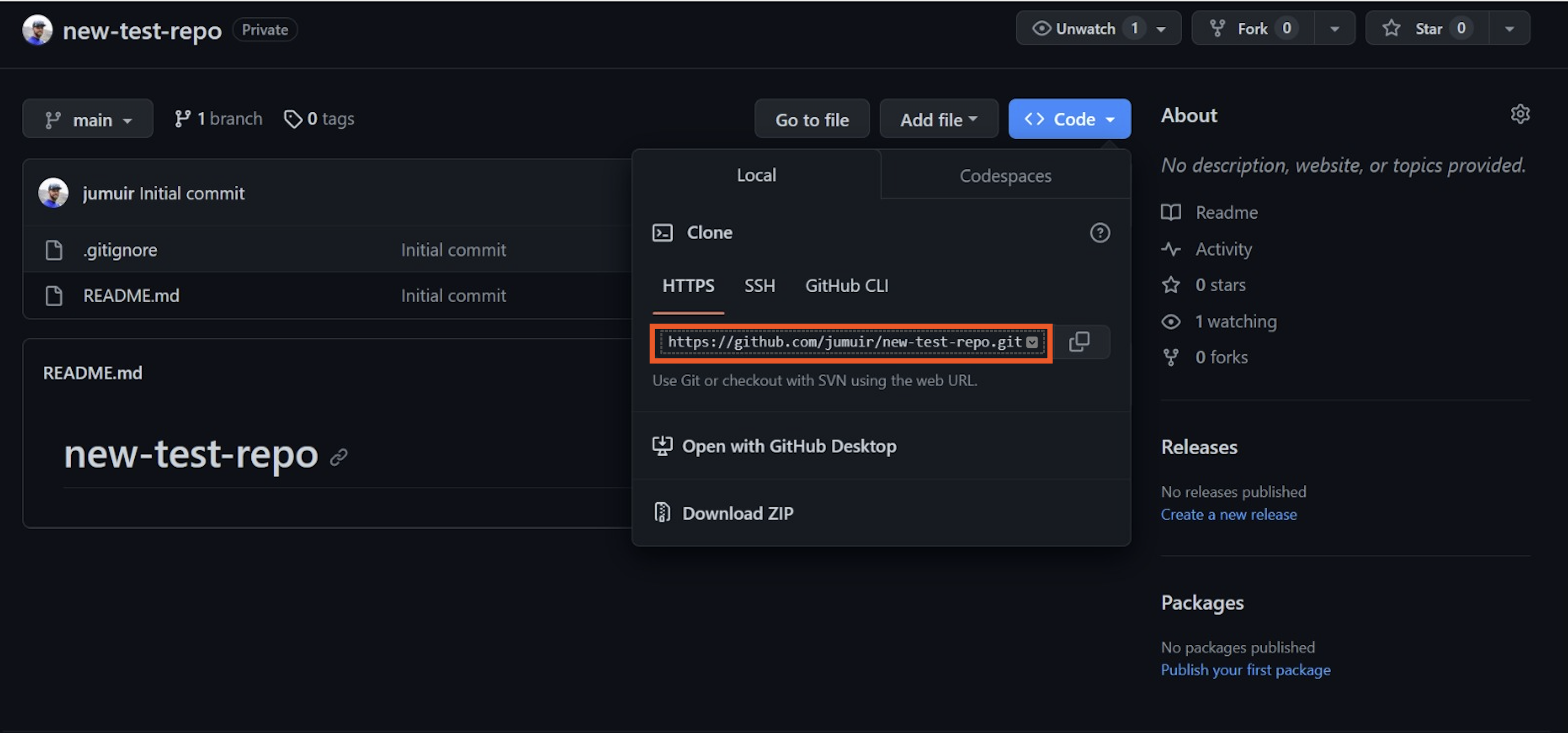
Go to the web page for your GitHub repository, and note the URL.
Open Bash on Windows. (If you're using Linux or Mac, open Terminal.)
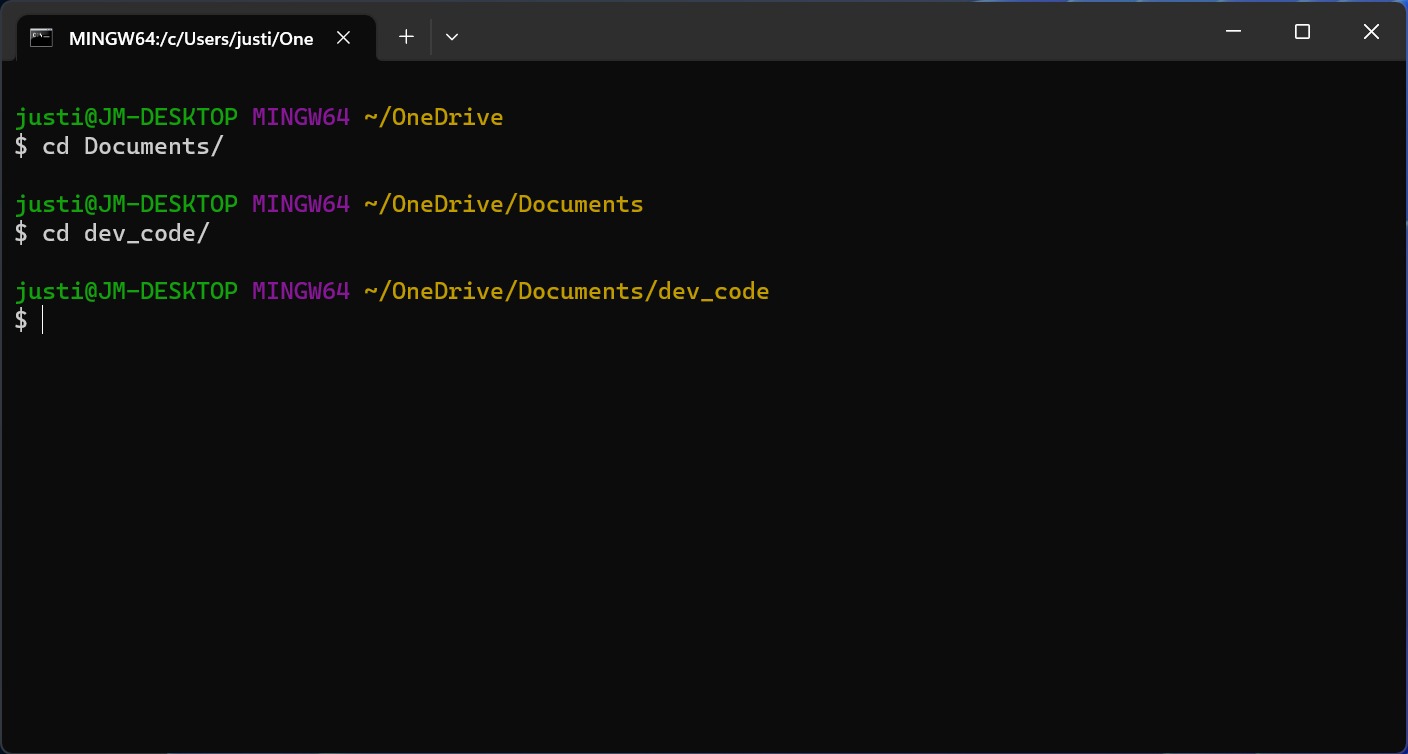
Use the
cdcommand to switch to the directory you want to use to work on your project locally.Enter
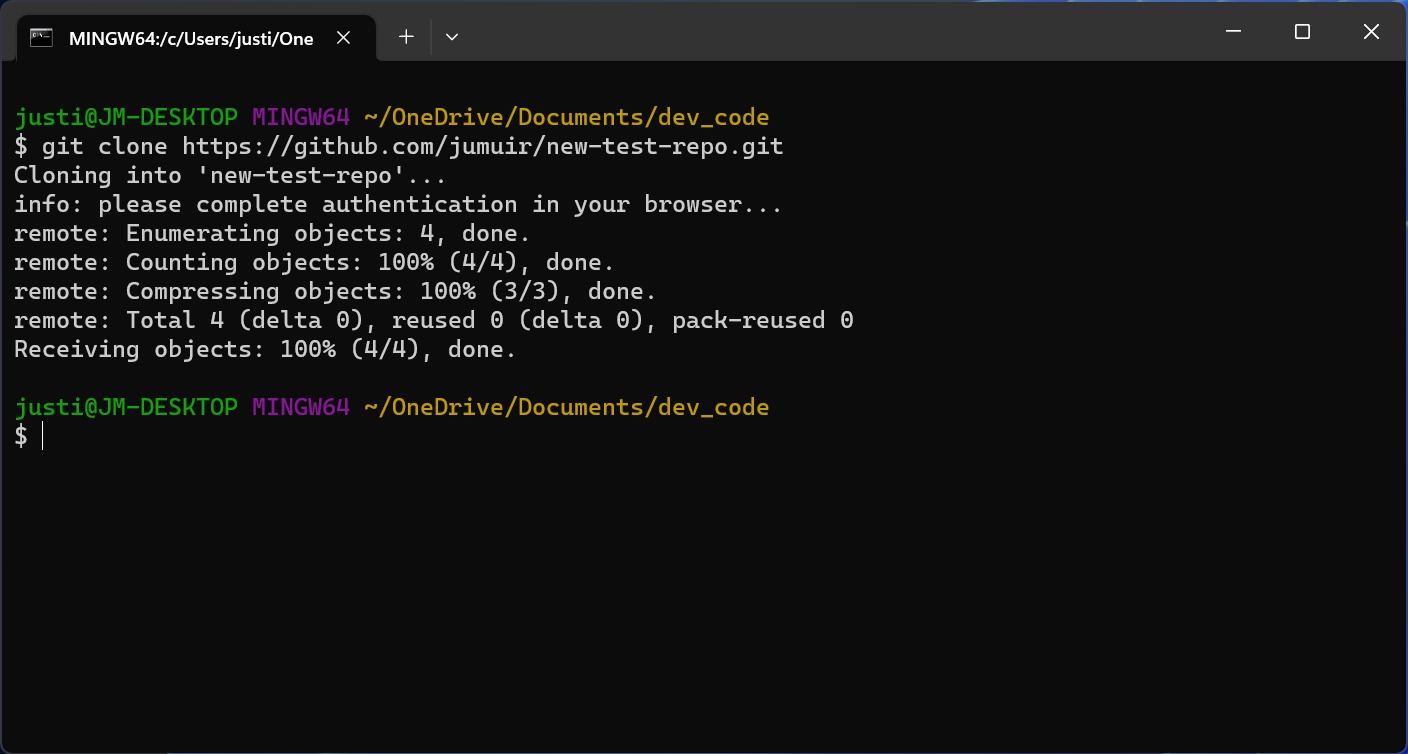
git clone [URL of your repository]to copy your repository to your local machine.Use the
cdcommand to go into your repository directory. You'll know you're in the right place if your new command line ends with the name of the main branch of your repository. For example, the name of my main branch is "main," so(main)appears at the end of my command line.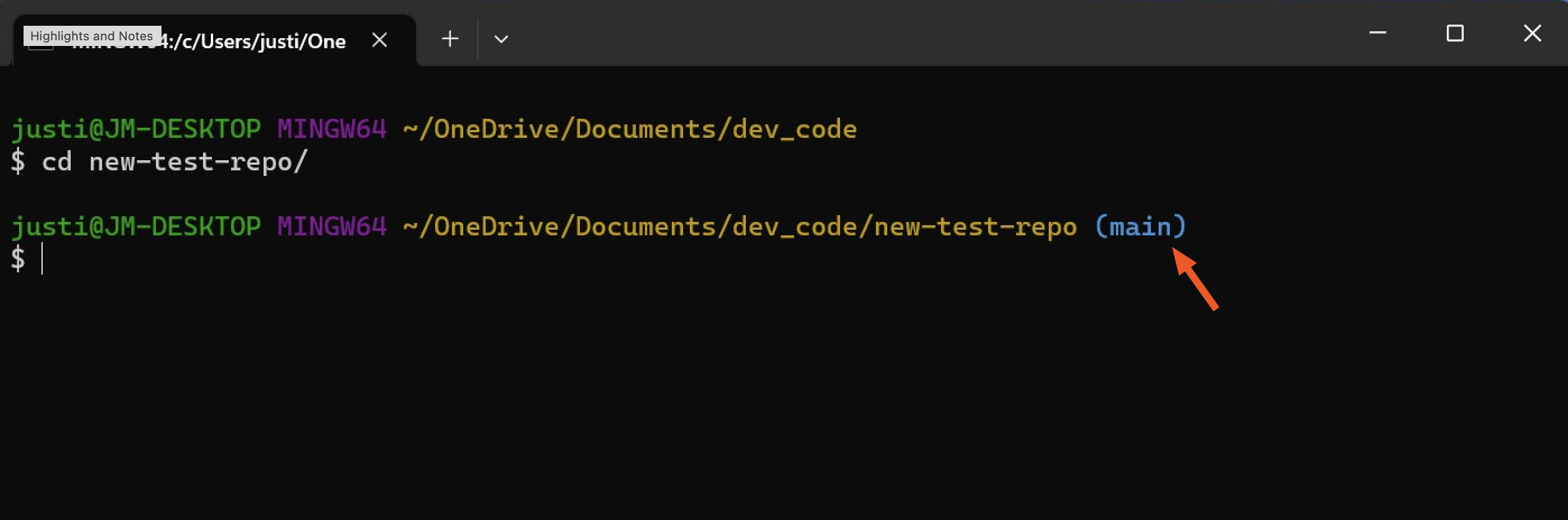
Once you've added your files to your directory and are ready to push to GitHub, in your Bash window, enter
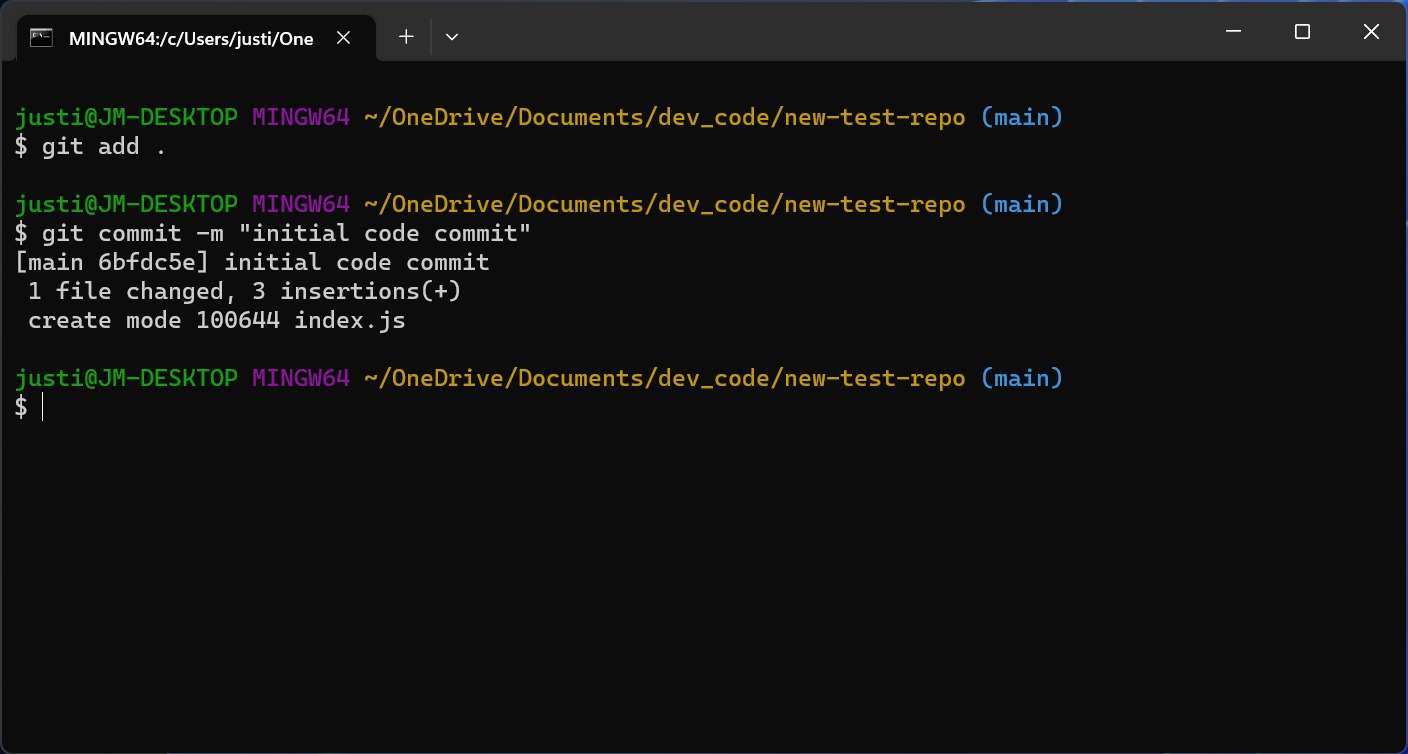
git add .to select all the files in your repository.Enter
git commit -m "[commit message]"to save the changes to your local repository. You can enter anything for the commit message, but adding-m "[commit message]"specifies what this code change is doing, so it's helpful to be clear and concise.Enter
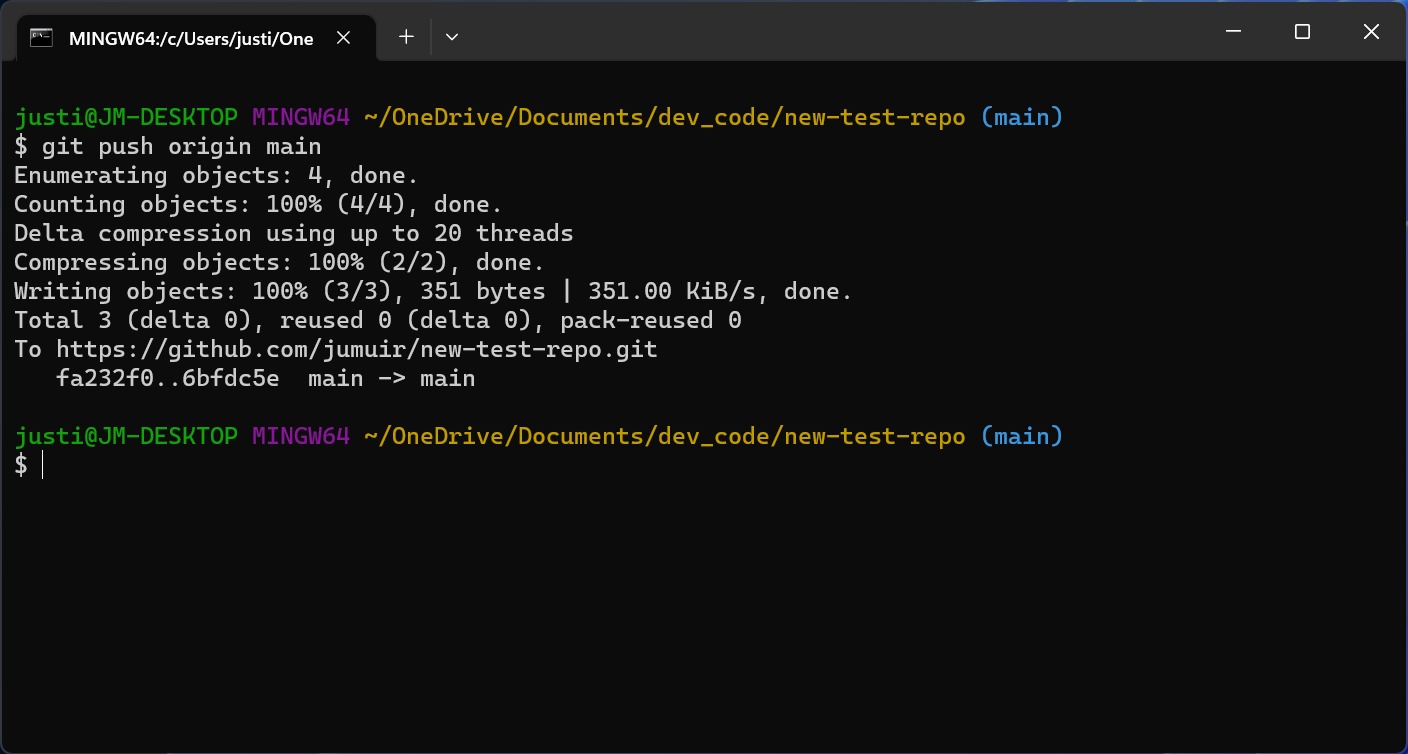
git push origin [branch name]to save your code changes to GitHub.
If you haven't already done so, GitHub will prompt you to authenticate your identity. Enter your GitHub username and password. Once the authentication is done, the upload process will start. After it's complete, you'll see specific details about where the data was uploaded.
That's it! You've successfully pushed your local files and folders to your GitHub repository.
To double-check that you pushed to GitHub successfully, open your GitHub repository web page. Your code changes should appear there.
Automate GitHub with Zapier
Zapier lets you connect GitHub to thousands of apps, so you can automate more of your Git processes. For example, you can automatically get a notification or create a task in your project management tool whenever there's a new pull request in your repository. Or you can notify others about new commits to your repo.
Learn more about how to automate GitHub and connect it to thousands of other apps, or get started with one of these templates.
Recevez des messages directs sur Slack pour les nouvelles mentions sur GitHub
Envoie des messages sur la chaîne Discord pour les nouveaux commits sur Github
Créer des cartes Trello à partir des nouveaux numéros de GitHub
Zapier est la plateforme d’orchestration AI la plus connectée, s’intégrant à des milliers d’applis de partenaires tels que Google, Salesforce et Microsoft. Utilisez des interfaces, des tables de données et de la logique pour créer des systèmes sécurisés, automatisés et alimenté par l'IA pour vos flux de travail critiques pour l'ensemble de la pile technologique de votre organisation. En savoir plus.
Lectures connexes :
This article was originally published in June 2019 by Khamosh Pathak. The most recent full update was in September 2023, and the article was fact-checked and lightly updated in April 2025.