ChatGPT threw the world for a loop in 2022, and now DeepSeek is throwing ChatGPT (and plenty of humans) for a loop.
DeepSeek-R1 is a new reasoning model from the Chinese AI company, DeepSeek. As an open model that anyone can use, its launch has shaken up Silicon Valley, knocked billions off major tech companies' stocks, and caused a whole lot of consternation. Why this all matters gets into the intricacies of AI model development, so first, let's look at what exactly DeepSeek-R1 is.
What is DeepSeek?

DeepSeek-R1 is an AI reasoning model built by DeepSeek, a Chinese AI company. It's a lot like OpenAI o1 and o3-mini, although unlike o1, it's open—which means anyone can download the model and run it on their own hardware. Compared to regular large language models (LLMs), reasoning models are vastly more capable because they use a chain-of-thought process to work through complex problems.
In terms of performance, R1 is roughly on par with o1 and o3-mini, and the smaller R1-32B is roughly equivalent to the now replaced o1-mini on a range of major benchmarks like AIME 2024 and MMLU. Head-to-head tests (and my own testing) all show much the same results: R1 is a very capable alternative to o1 and o3-mini. Sure, there's still the odd mistake or hallucination, but there isn't a drastic difference between the models.
And it's the same with DeepSeek's other models. For example, there's a ChatGPT-like chatbot (that I'll get to in a bit); there's an open text model called DeepSeek-V3 that compares favorably to other top models like GPT-4o, Claude 3.1, and Llama 3.1 405B; and there's a text-to-image model called Janus-Pro-7B that stacks up well against DALL·E 3 and other similar models.
While this level of performance across the board is impressive in its own right, it's how DeepSeek was able to achieve it that makes it such a big deal.
Why are DeepSeek-R1 and DeepSeek-V3 so impressive?
The short answer: geopolitics.
The U.S. has banned the export of Nvidia H100 GPU chips to China, in part to try to prevent Chinese tech companies from developing powerful AI models. H100s are the chips that OpenAI, Anthropic, and Meta rely on for developing their current AI models, and the working assumption was that a frontier model would be almost impossible to build without them. (For what it's worth, Google also uses its own custom Tensor Processing Units.)
But despite the U.S. government's attempt to limit what Chinese tech companies could do with AI and preserve American leadership in the space, DeepSeek has been able to create models as powerful as any currently available from OpenAI, Anthropic, or Google, using the lower spec H800 chips. Worse still (from a U.S. government and Silicon Valley perspective), DeepSeek has been able to do it for less money, using less computing power, and they've released the resulting research papers and models under an open license so anyone can use them.
Until now, OpenAI stood alone as the developer of reasoning models. Its market position was so unique that OpenAI is charging $200/month for unlimited access to o1. Now, though, anyone can use a similar model for free through DeepSeek's chatbot, or if they have the technical skills, download it and run it on their own computer. And this was just one of the smaller shockwaves affecting Silicon Valley. (OpenAI quickly responded by making o3-mini available for free users too.)
What makes DeepSeek-R1 and V3 different?
The very optimizations that DeepSeek had to use to make training frontier models on H800 chips possible are part of what make R1 and V3 stand out. Since DeepSeek couldn't throw raw computing power at the problem, they had to develop a number of workarounds. While many of these are based on existing techniques, here are a few of the noteworthy things DeepSeek did with R1, V3, and their prior models:
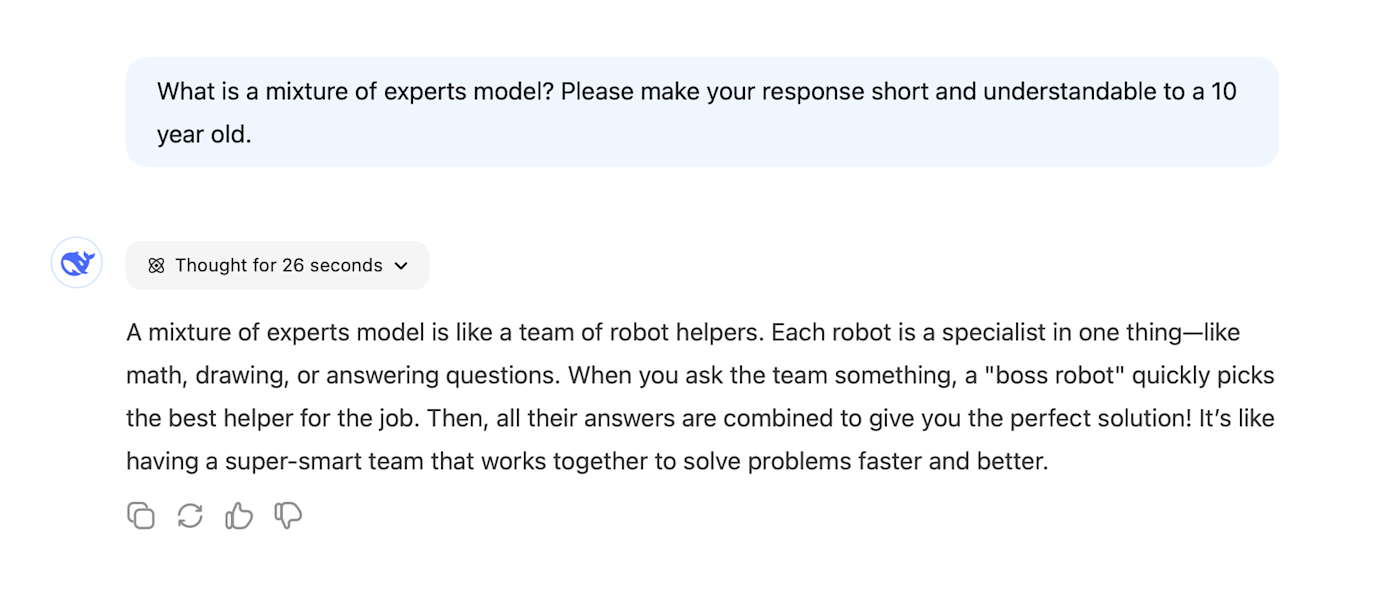
Developed a "mixture of experts" (MoE) model that combined shared experts with general capabilities and specific experts with more narrow capabilities, which makes the model more efficient. (These allow for models that have extremely high numbers of parameters but only activate a limited subset on inference so they can run more efficiently.)
Developed multiple ways to make training more efficient by reducing the amount of computing resources required to balance the training workload between the different experts.
Developed multiple ways to make inference more efficient, including a technique for reducing the memory use required by large context windows.
Relying heavily on "distillation," where smaller models are trained on the output of more powerful models. (This is somewhat controversial.)
Trained a precursor to R1 called R1-Zero using machine-based reinforcement learning instead of reinforcement learning from human feedback (RLHF).
Combined, these innovations all make DeepSeek's models as powerful as those from OpenAI, Anthropic, Meta, and Google, but significantly cheaper to train and run inference on. The headline number was that DeepSeek managed to train V3 for just $5.576 million. For context, just last year there was talk of future models costing $1 billion to train, while GPT-4 reportedly cost $100 million to train.
This low price understates things dramatically—it only refers to the GPU rental costs associated with the final training run for V3 and not any of the prior research, data gathering, salaries, and all the other expenses necessary to develop frontier models and run an AI company. But it was still a major shock to the stock market as it raised concerns about how much the AI revolution was going to continue to rely on expensive hardware and compute rental from Nvidia, Microsoft, and other big tech companies.
DeepSeek is obviously now controversial
The DeepSeek chatbot app shot to the top of both the App Store and Play Store around the world. But as you can imagine, a Chinese AI company launching a free AI model and chatbot that are comparable to the best currently available from any U.S. company didn't pass without controversy.
As a Chinese-developed chatbot, it has some censorship issues. It refuses to talk about Tank Man and considers Taiwan part of China, for example, though I was able to get it to discuss whether or not China is committing genocide against Uyghur Muslims. Similarly, it's explicitly sending data to China.
How much all this matters to you really depends. Every AI company trains their chatbots and models to respond in specific ways to avoid controversy. If you aren't planning on using the DeepSeek chatbot to campaign for Tibetan freedom, you're unlikely to run into any issues with DeepSeek's responses. And, of course, you can always run R1 yourself without the censorship or data issues.
OpenAI has also accused DeepSeek of training R1 using ChatGPT's outputs without permission. The irony of this isn’t lost on anyone. I think OpenAI would like people to consider this a big deal, but I can't say it's a reason to stay away from DeepSeek.
How to try DeepSeek-R1
The simplest way to try DeepSeek-R1 is through the free DeepSeek chatbot app. It's available on the web, and for iOS and Android devices. Given DeepSeek's sudden popularity, signups are sometimes slow, and the app is sometimes too busy to respond. Of course, if you have the technical skills, you can just grab R1 from Hugging Face.
While DeepSeek's chatbot is more barebones than ChatGPT in many ways, it works. You don't have any bells and whistles, but you can still use incredibly capable AI models.
Related reading:
This article was originally published in January 2025. The most recent update was in February 2025.









