It's timeless advice: if a website isn't loading properly, clear your cache. We've all done it. You might have even let out a little cheer when the site started working again. And, if you're like me, you promptly proceeded to not think about the browser cache ever again—until the next thing broke.
But in the back of your mind, you might be wondering: what the heck is the cache? Why does clearing it fix things?
I care about you, and want you to know things, so let's get into it.
Table of contents:
What is a cache?
A cache (pronounced cash, like money) is a storage location on your computer or phone where your browser keeps bits and pieces of websites—things like images, fonts, HTML, CSS, and JavaScript files.
How does a cache work?
The first time you visit a website, your browser downloads everything it needs to display the page—for example, text, images, stylesheets, and scripts. Some of those files are marked as "cacheable," which tells your browser it can save them for later.
When you revisit a page from that same website, your browser first checks the cache to see if it already has what it needs. If it does, it uses the cached files instead of downloading them again, which cuts down on loading time and saves bandwidth.
Take, for example, the page you're currently on. There's a Zapier logo at the top-left corner of it. If you go to another Zapier blog post or the Zapier homepage, that same logo will be there. Your browser could re-download it each time—but that would be inefficient. So instead, it saves the logo in your cache and pulls it from there whenever it needs to.
Pros and cons of a cache
Like most behind-the-scenes tools, your browser's cache comes with its pros and cons.
Cache pros
Faster browsing: Since your browser isn't starting from scratch each time, websites—especially media-heavy pages—load noticeably quicker.
Reduced bandwidth usage: Cached content doesn't need to be re-downloaded, which is great if you're on a limited data plan or are running on a slower internet connection.
Better performance for repeat visits: Sites you often visit will feel snappier and more responsive.
Cache cons
Outdated content: Your browser might serve up an older, cached version of a page, which means you might miss recent updates or see stale info.
Website glitches: In some cases, the cached version of a file may not play nice with newer site updates, leading to broken layouts, missing buttons, or things just not working as they should.
Storage buildup: Over time, your cache can get cluttered with old or unnecessary files, which may slow things down instead of speeding them up.
What does clearing the cache do?
Clearing the cache deletes the temporary files stored by your browser. It's a common fix when a website starts acting up because it forces your browser to download the most up-to-date version of a site's assets the next time you visit.
If you don't clear the cache when a website is glitching, you might continue to experience frustrating things like broken layouts, missing features, or buttons that ignore you no matter how many times you speed-click them in a quiet rage.
If you're struggling to sign on to a public Wi-Fi network, the cache might be the problem. Here's how the browser cache comes into play when trying to force open a public Wi-Fi login page—and how to fix it.
Cache vs. cookies: What's the difference?
In most browsers, the options for clearing the cache and clearing cookies are in the same place—but they're not the same thing. Here's the difference:
Cache: This is where your computer stores files downloaded directly from the websites you visit—fonts, images, that kind of thing. The files in your cache aren't that different from the files in the cache of someone else who visits the same websites as you.
Cookies: Unlike your cache, cookies store information about you and the things you've done online. If you browse an online store and add a bunch of things to a shopping cart, that's saved using a cookie. Cookies also keep track of which site you're logged in to—which is why, if you clear your cookies, you'll need to log back in to all of your accounts. Clearing your cache doesn't affect any of this.
How to clear your browser cache
Depending on which web browser you're using, the steps to clear your cache might vary. But no matter the browser, it's straightforward to do.
How to clear your browser cache on Google Chrome
From the menu bar of a Google Chrome window, click More (
⋮).Click Delete Browsing Data.
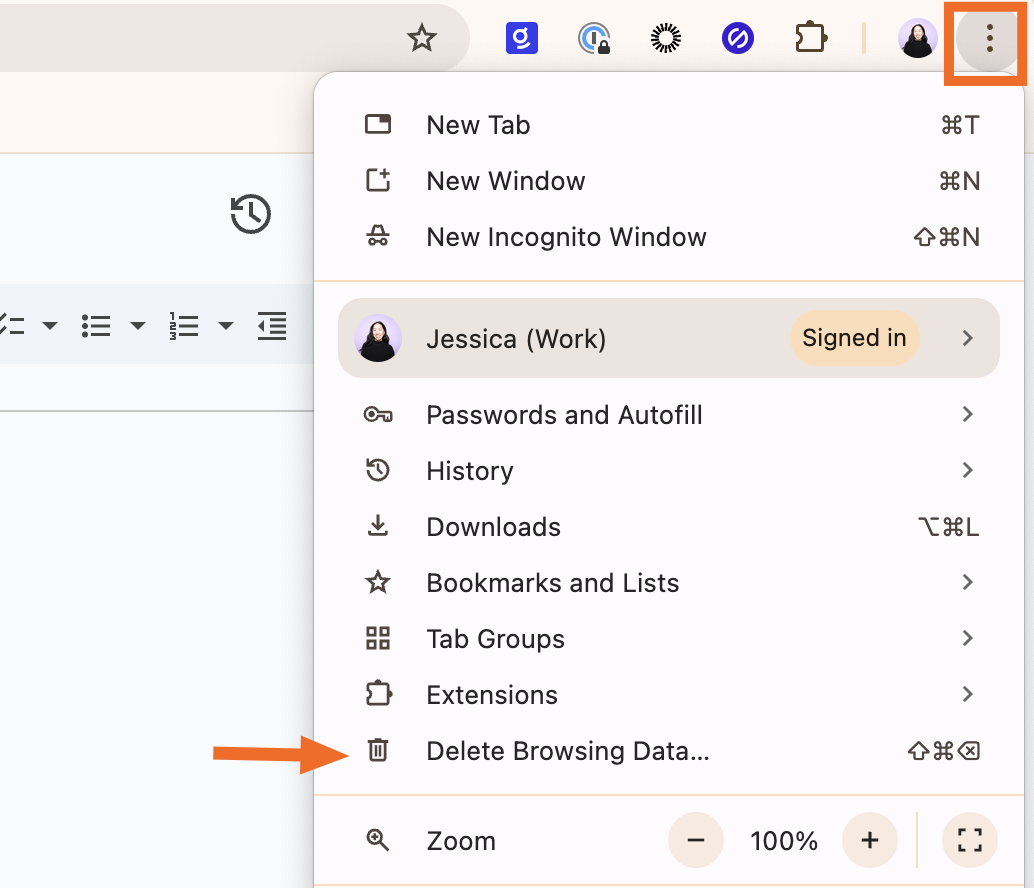
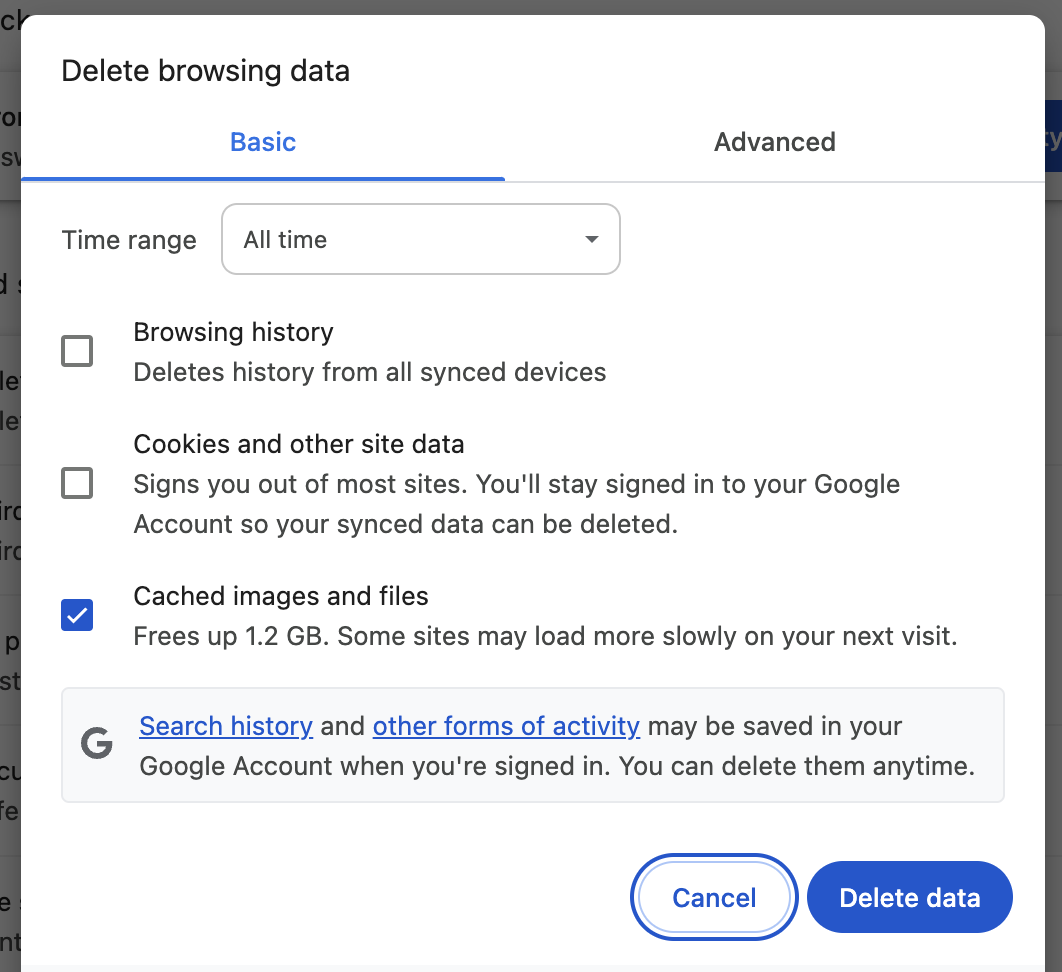
You'll be redirected to a popup on Google Chrome's Settings page. Make sure only Cached images and files is selected (unless you want to clear your cookies), and then click Delete data.
How to clear your browser cache on Safari
From your Mac's menu bar, click History, and then click Clear History.
In the popup that appears, click the dropdown beside Clear.
Select all history, and then click Clear History.

How to clear your browser cache in Microsoft Edge
From the menu bar of a Microsoft Edge window, click Settings and more (
...).Click Settings, and then select Privacy, search, and services.
In the Clear browsing data section, click Choose what to clear.
In the popup that appears, make sure only Cached images and files is checked, and select the desired time range from the dropdown.
Click Clear now.

How to clear your browser cache in Firefox
For some inexplicable reason, there are two very different ways to clear your cache in Firefox. Here's the most straightforward way.
From the menu bar of a Firefox window, click the application menu, which looks like three lines stacked horizontally (
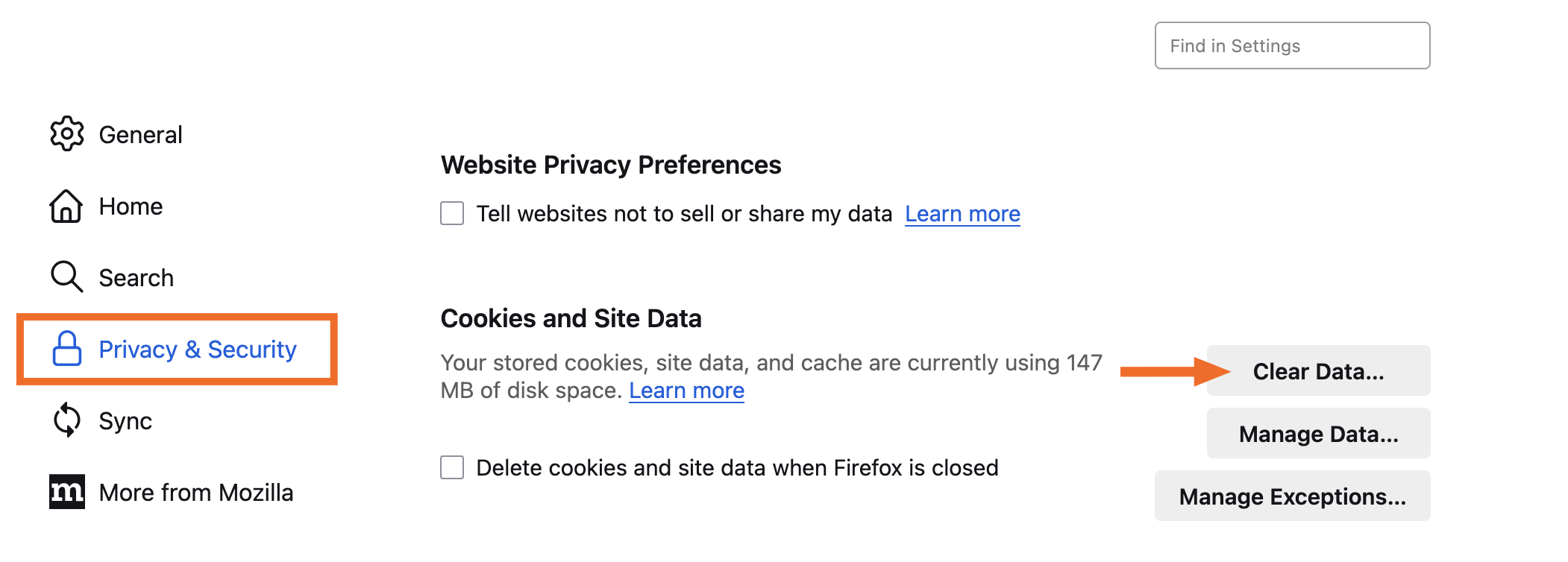
≡), and then click Settings.From the navigation pane, click Privacy & Security.
In the Cookies and Site Data section, click Clear Data.
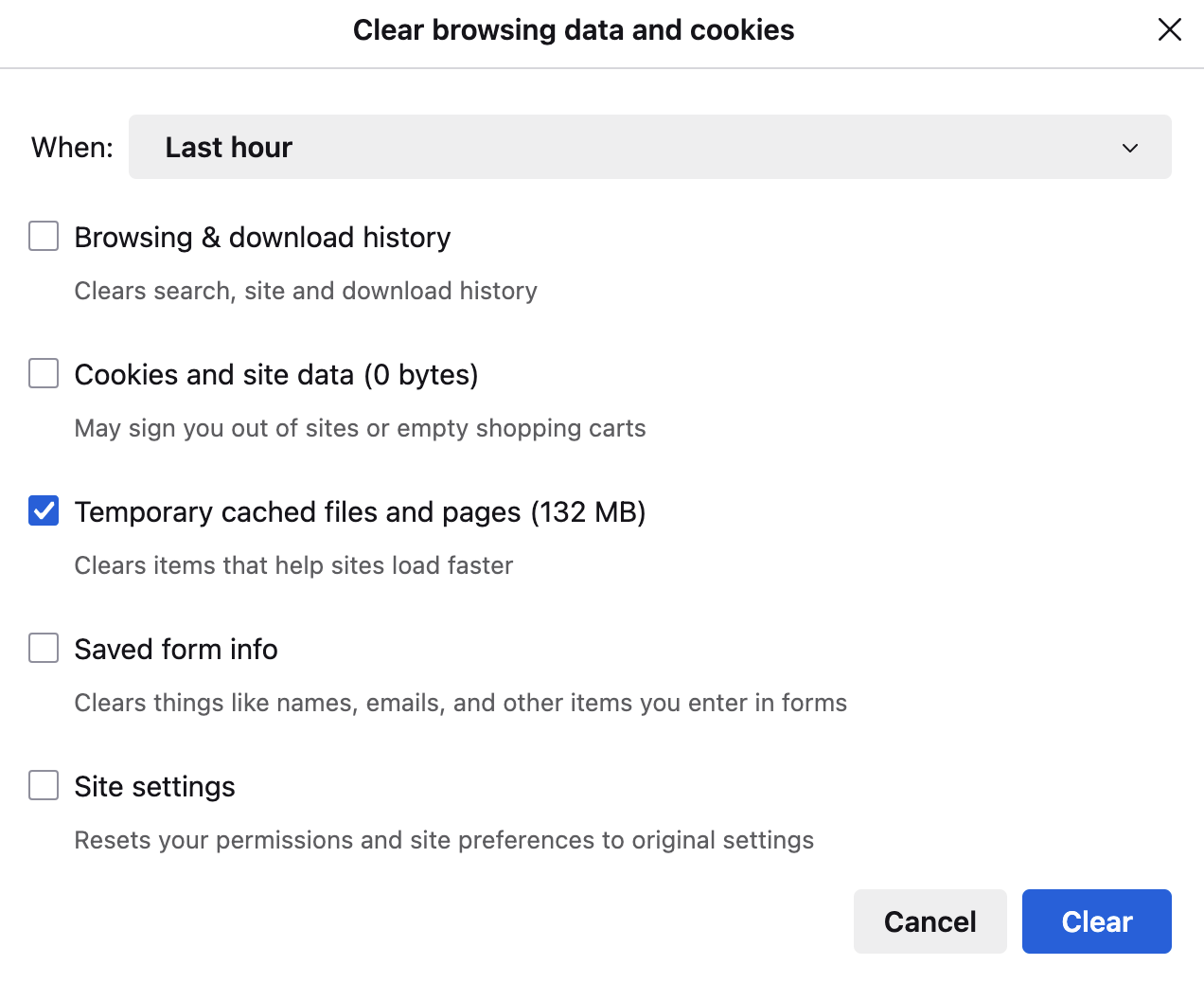
In the popup that appears, make sure only Temporary cached files and pages is checked (unless you want to clear your cookies), and then click Clear.
How often should I clear my cache?
I generally recommend not clearing your cache unless you have a specific reason to—like when you're one rage-click away from throwing your computer out the window.
The files in the cache allow the websites you visit most often to load faster, which is a good thing. Plus, your browser deletes old files periodically, so it's not like the cache is going to keep growing forever.
Sure, the cache is taking up room on your hard drive, and that can be annoying. But the reason you have a hard drive is so you can store things on it.
Related reading:
This article was originally published in July 2020 by Justin Pot. The most recent update was in April 2025.