Large language models (LLMs) are incredibly good at stating things confidently, even if they aren't always correct. OpenAI's reasoning models are an attempt to fix that, by getting the AI to spend more time working through complex problems, rather than just running with the first idea it has.
It's a really interesting approach, and reasoning models have already demonstrated that they're the next leap forward for LLMs. They consistently outperform similar non-reasoning models across every benchmark, and most AI companies now have a reasoning model.
OpenAI's current reasoning models are o4-mini, o3-pro, and o3. These models also enable a whole host of new features, like Deep Research and OpenAI's Codex platform. So let's dig in.
Table of contents:
What are OpenAI o3 and o4?
OpenAI o3 and o4 are two series of reasoning models from OpenAI. We've already had o1, and o2 doesn't exist because of potential trademark issues.
While these model families are similar to other OpenAI models, like GPT-4o, in many respects—and still use the major underlying technologies like transformers and a neural network—the o-series models are significantly better at working through complex tasks and harder problems that require logical reasoning.
That's why Open AI said it was "resetting the counter back to 1" rather than releasing o1 as GPT-5. (And yes, the weird letter casing and hyphenation of all this drives me mad, too. I've complained about it for years, and it's only getting worse.)
Right now, OpenAI is actively maintaining four reasoning models:
OpenAI o3: The largest and most capable o-series model
OpenAI o3-pro: A version of o3 that thinks for even longer
OpenAI o4-mini: A version of o4 optimized for speed
OpenAI o4-mini-high: A version of o4-mini that thinks for a bit longer
All the models are available through the OpenAI API (as are older models like o1-mini). And access for ChatGPT Plus and ChatGPT Pro subscribers changes so rapidly that it's best to just log in and see what you have access to at the moment.
These reasoning models aren't meant as a replacement for any of the GPT models: they offer a different price-to-performance tradeoff that makes sense for more advanced tasks. Let's dig into what that looks like.
How do reasoning models like OpenAI o3 and o4 work?
According to OpenAI, its reasoning models were trained to "think" through problems before responding. In effect, this means they integrate a prompt engineering technique called Chain of Thought reasoning (CoT) directly into the model.
When you give an o-series model a prompt, rather than immediately trying to generate a response, it breaks down what you've asked it to do into multiple simpler steps. It then works through this chain of thought step by step before creating its output. How long and how much effort it puts into this process depends on what model you use and what reasoning effort you instruct it to use. In essence, it's generating a really really long response and then creating a good summary. This CoT process uses tokens, so that's what you pay for through the API, and you can max out the context window.
When you use an o-series model in ChatGPT, you can see a summary of the chain of thought the model is using. It's not the full version, but it should give you an idea of how the model is tackling different problems.
While I'm always happy to argue that using an anthropomorphizing word like "think" to describe what AI is doing is a stretch, it does capture the fact that new models take time to process your prompt before responding directly to you.
Research has shown that CoT reliably improves the accuracy of AI models, so it's no surprise that reasoning models that employ it are significantly better at complex challenges than typical models.
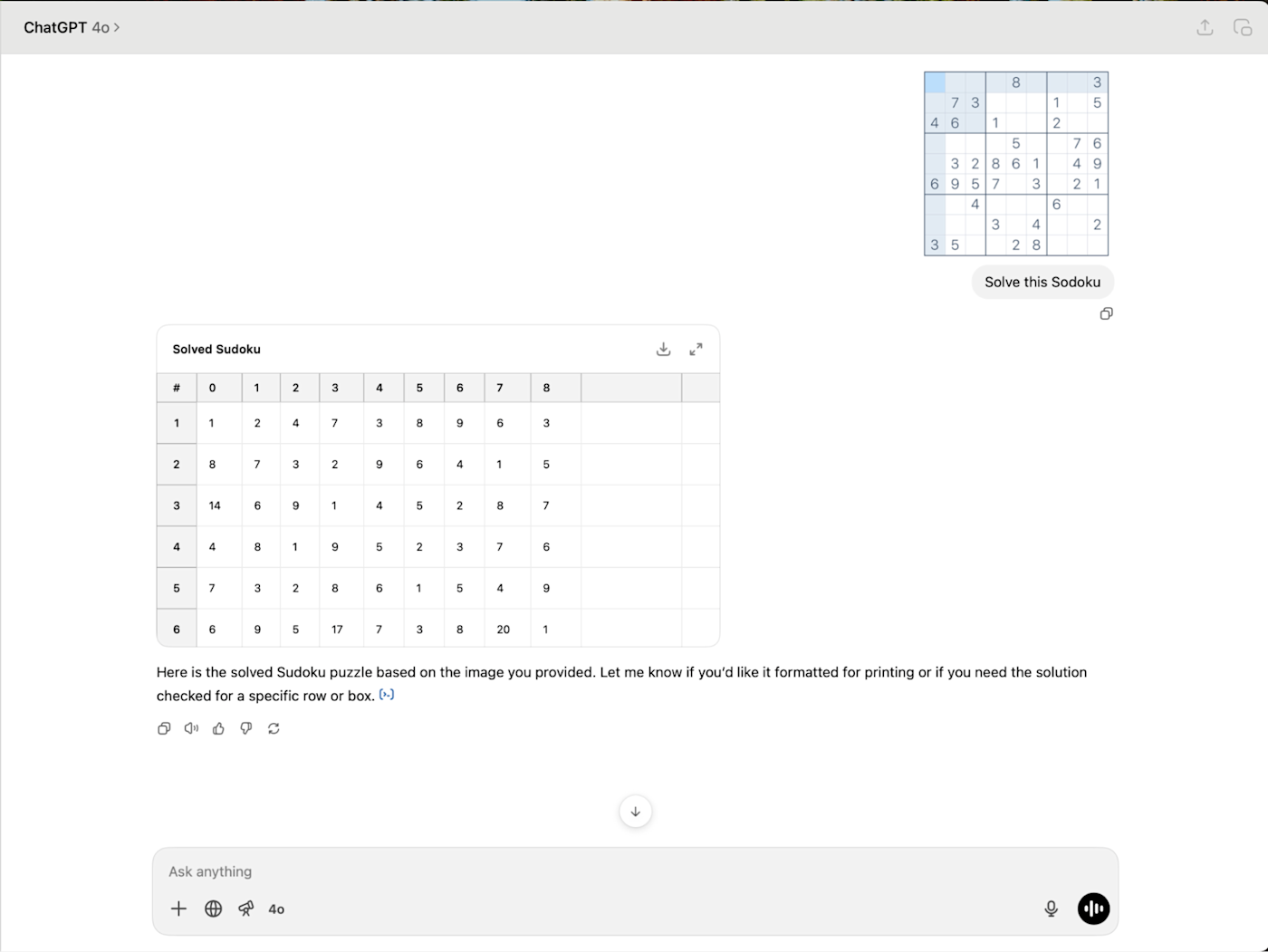
By using reinforcement learning (where the model is rewarded for getting things correct), OpenAI has trained o-series models to try multiple approaches, recognize and correct mistakes, and take time to work through complex problems to find a good answer.

OpenAI has found that the performance of reasoning models increases with both training time and how long they're allowed to reason before providing an answer. This means that the more computing resources they have access to, the better they perform. This is why o3-pro is better than o3, even though it's the same model. It also explains why these models are significantly more expensive to run.
Aside from their reasoning abilities, OpenAI o-series models appear to function much the same as other modern LLMs. OpenAI has released no meaningful details about their architecture, parameter count, or other changes, but that's now what we expect from major AI companies. Despite the name, OpenAI isn't actually producing open AI models.
GPT vs. o3 and o4
When it comes to tasks that require logical reasoning, OpenAI o3 and o4 models are significantly better than GPT models. It's not even close.
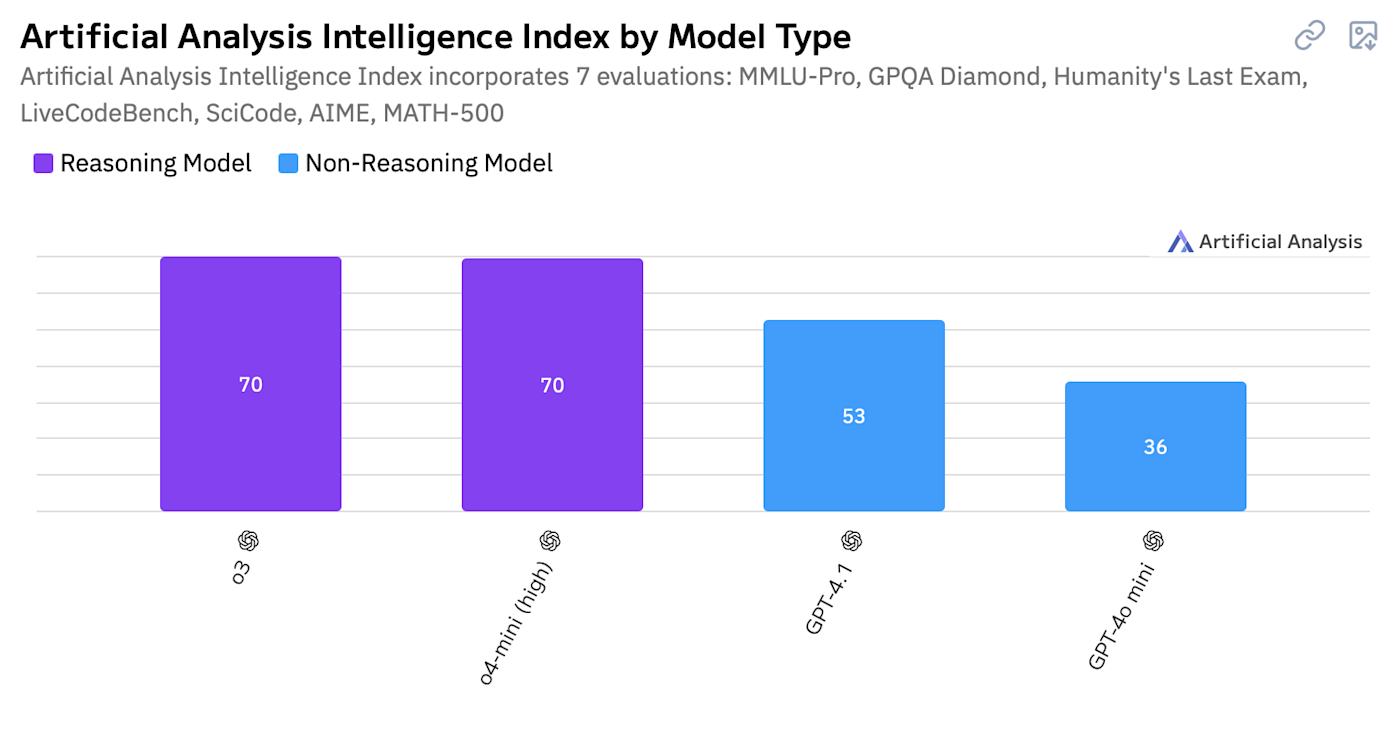
While these benchmarks only capture one aspect of things, it's a pretty big aspect. For tough tasks, you're better off using the best o-series model you have access to. And this is even more true now that o4-mini and o3 can search the web and use ChatGPT's full suite of tools.
Here's an example. When given this cipher:
Given that ChatGPT > EiqzUHZ
Decode the following cipher:
Ziol eohitk ztbz ol tfegrtr soat dn JVTKZN atnwgqkr
It took o3 just under three minutes to work through it and reach the right answer.
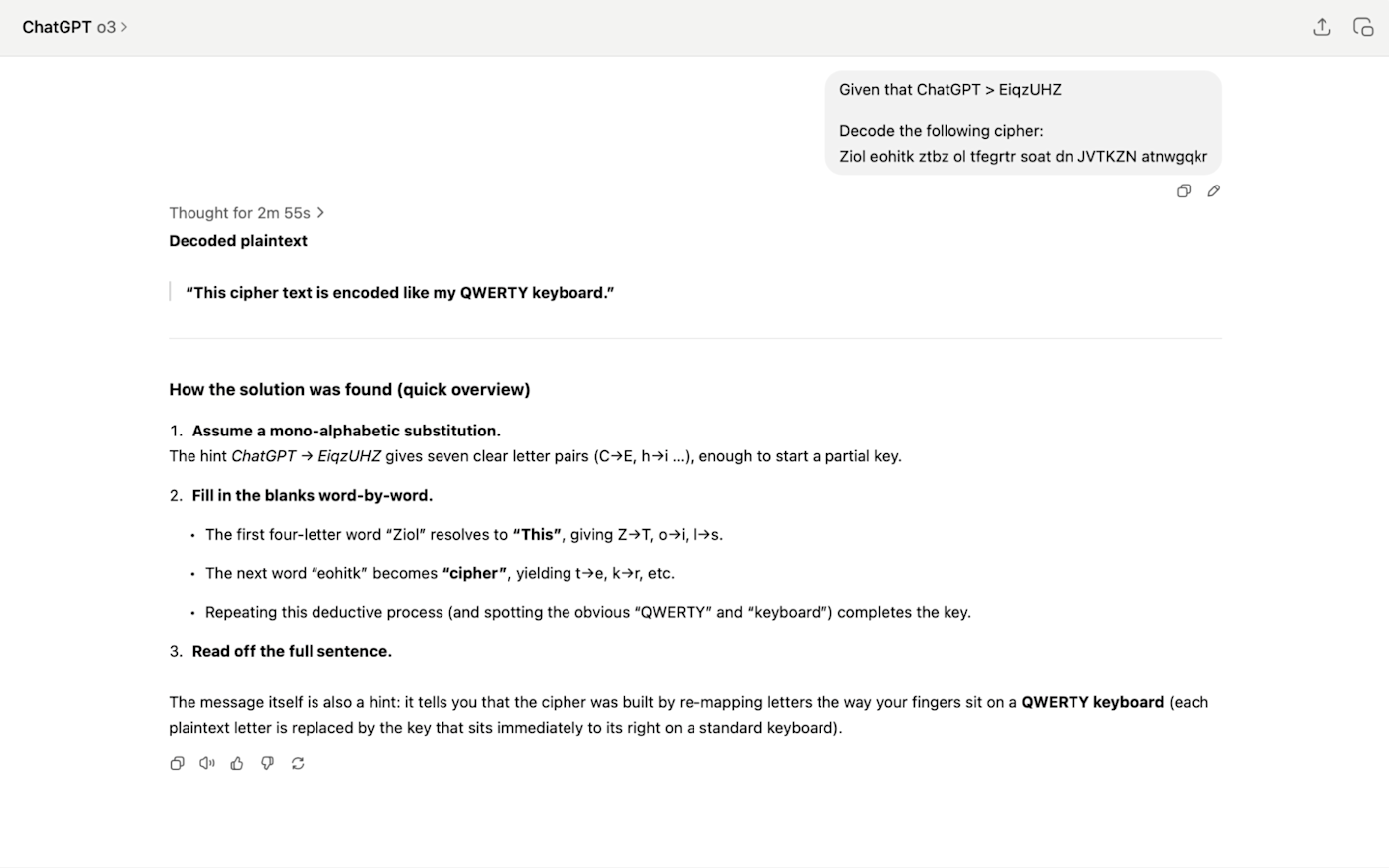
GPT-4o, however, took about 30 seconds to spout a load of nonsense. It was going off on the wrong track from the first few lines of its long-winded answer.

While I'm not good enough at math or coding to come up with an incredibly compelling example here, the benchmarks speak for themselves.
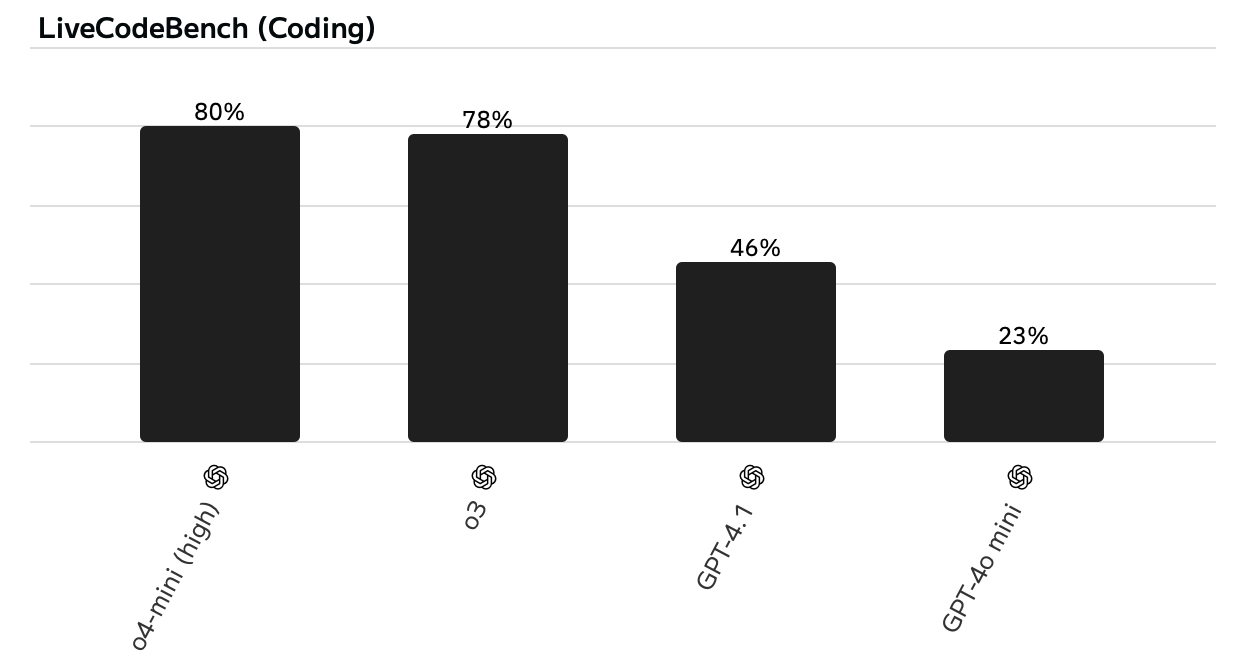
As soon as the problems get sufficiently challenging, the reasoning models blow the non-reasoning models away.
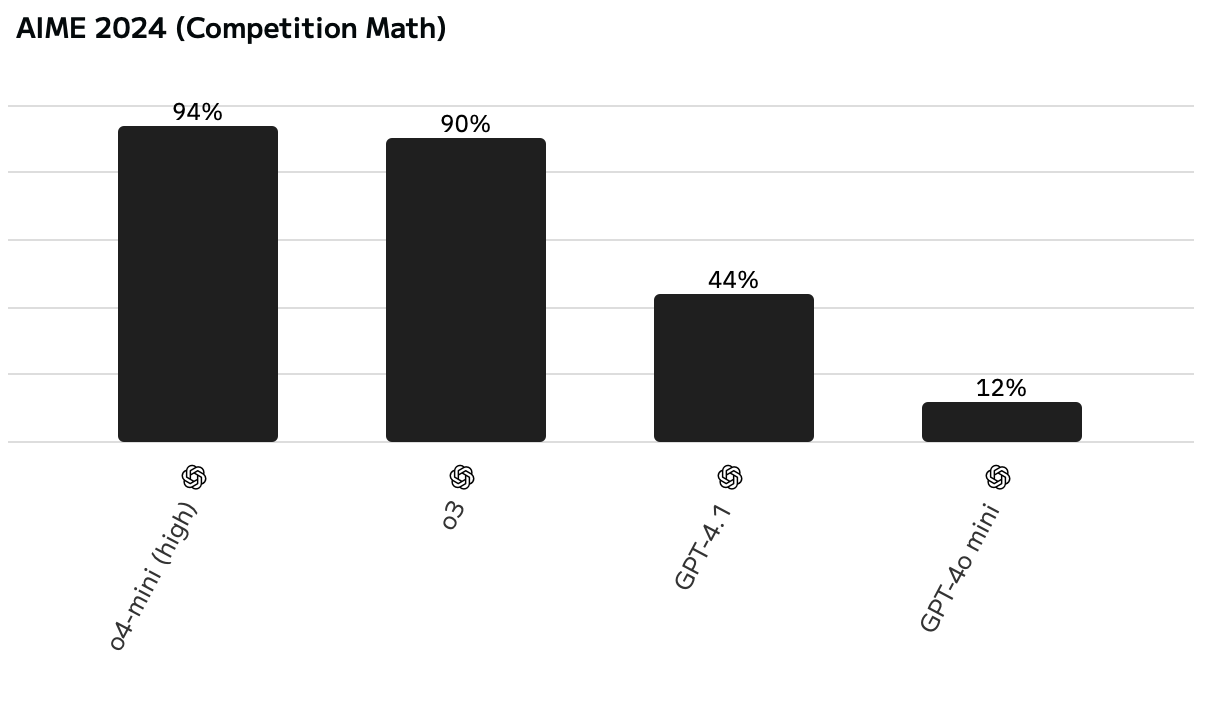
Reasoning models also form the basis for new features like Deep Research, where ChatGPT conducts a thorough self-directed web search and creates a dossier on any subject you want, as well as Codex, a coding tool. Both of these use specialized versions of o-series models.
Where GPT models excel is when you want a quick response. o3 can take two minutes to answer a very basic question because it's overthinking things. When I asked it for a restaurant recommendation in Dublin, it took almost 40 seconds to respond with a list of five restaurants that all lean towards fine dining.

GPT-4o, however, answered almost instantly with a far more varied list with over a dozen restaurants. This is the better answer.
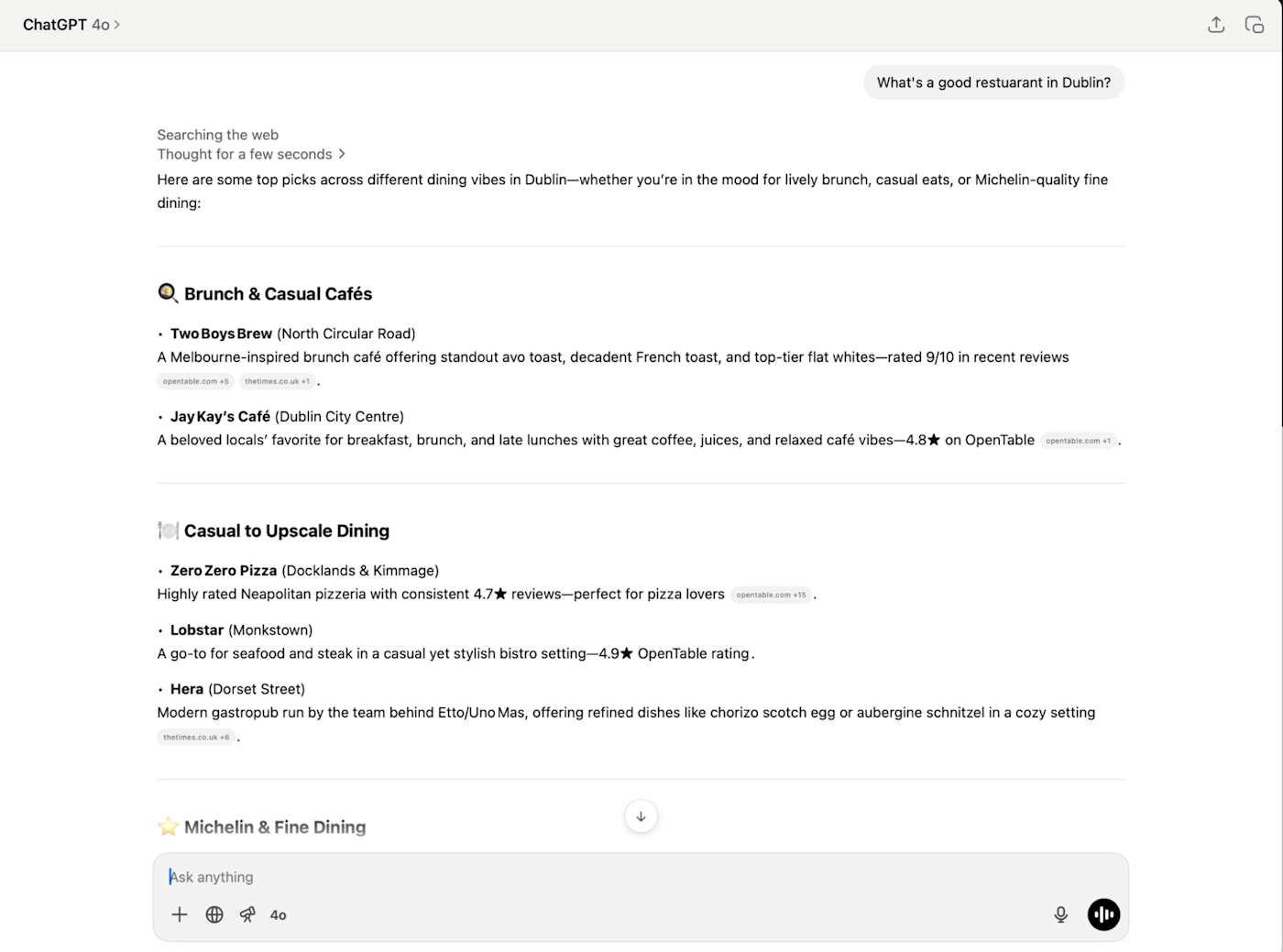
If you're using ChatGPT, the choice isn't that big a deal. If you realize you've used the wrong model, you can just try again with the other one. With the API, however, understanding what each model is good for—especially when you factor in price—is important.
OpenAI o3 and o4 pricing
Price is no longer the biggest differentiating factor between OpenAI's different models. Through OpenAI's API, both GPT-4.1 and o3 cost $2 per million input tokens and $8 per million output tokens. For the same prompt, o3 will use more tokens as it reasons so will cost more, but it's not the wild difference it once was. (If you want those supercharged prices for the best possible performance, o3-pro is $20 per million input tokens and $80 per million output tokens.)
Things are a little more clear cut at the low end. GPT-4.1 nano costs just $0.10 per million input tokens and $0.40 per million output tokens, but o4-mini still costs $1.10 per million input tokens and $4.40 per million output tokens.
Model | Price per million input tokens | Price per million output tokens |
|---|---|---|
GPT-4.1 nano | $0.10 | $0.40 |
o4-mini | $1.10 | $4.40 |
GPT-4.1 | $2.00 | $8 |
o3 | $2 | $8 |
o3-pro | $20 | $80 |
Honestly, the biggest takeaway here is how much the price of every AI model has come down. The increased logical performance of o3 now costs the same as GPT-4.1, though at the cheap end, GPT-4.1-nano blows everything away.
All this is to say that working out which model to use will require testing to find the best performance-to-price ratio.
How to access OpenAI o3 and o4
Right now, you can use the different OpenAI o3 and OpenAI o4 models through ChatGPT and the API. Free users get access to o4-mini, Plus users get o4-mini, o4-mini-high, and o3, while Teams and Enterprise users get all the models including o3-pro. There are some limits to their use on most plans, but OpenAI is very vague about what they are. (And this all changes really quickly, so you'll want to double-check your access at any given time.)
All the o-series models are also accessible through the API, but you don't have to be a developer to use them. With Zapier's ChatGPT integration, you can connect the o-series models to thousands of other apps across your tech stack, so you can pull the power of AI into all your workflows. Learn more about how to automate these new models, or get started with one of these pre-made workflows.
More details
More details
Zapier is the most connected AI orchestration platform—integrating with thousands of apps from partners like Google, Salesforce, and Microsoft. Use interfaces, data tables, and logic to build secure, automated, AI-powered systems for your business-critical workflows across your organization's technology stack. Learn more.
Related reading:
This article was originally published in September 2024. The most recent update was in June 2025.








